Astronetes Resiliency Operator provides a transparent and effortless solution to protect Cloud Native platforms from possible disaster outages by leveraging Kubernetes native tools.
This is the multi-page printable view of this section. Click here to print.
Resiliency Operator
- 1: Getting started
- 1.1: Intro
- 1.2: Release notes
- 2: Architecture
- 2.1: Overview
- 2.2: Components
- 2.3: Observability
- 2.4: Audit
- 3: Installation
- 3.1: Preparing to install
- 3.2: Installing on Kubernetes
- 3.3: Installing on OpenShift
- 3.4: Uninstalling on Kubernetes
- 3.5: Uninstalling on OpenShift
- 4: Configure
- 4.1: Integrating with Grafana
- 4.2: Integrating with Grafana Operator
- 4.3: Integrating with OpenShift Alerting
- 4.4: Update license key
- 5: Assets
- 5.1: Introduction
- 5.2: Buckets
- 5.2.1: Import GCP Cloud Storage
- 5.2.2: Import generic bucket
- 5.2.3: Configurations
- 5.2.4: API Reference
- 5.3: Databases
- 5.3.1: Import Zookeeper
- 5.4: Kubernetes Clusters
- 5.4.1: Import
- 5.4.2: Configurations
- 5.4.3: API Reference
- 6: Synchronization
- 6.1: Introduction
- 6.2: Bucket to Kubernetes
- 6.2.1: Introduction
- 6.2.2: Configuration
- 6.2.3: Observability
- 6.2.4: API Reference
- 6.3: Kubernetes to Bucket
- 6.3.1: Introduction
- 6.3.2: Configuration
- 6.3.3: Observability
- 6.3.4: API Reference
- 6.4: Kubernetes to Kubernetes
- 6.4.1: Introduction
- 6.4.2: Configuration
- 6.4.3: Observability
- 6.4.4: API Reference
- 6.5: Zookeeper to Zookeeper
- 6.5.1: Introduction
- 6.5.2: Configuration
- 6.5.3: API Reference
- 7: Automation
- 7.1: Introduction
- 7.2: Plugins
- 7.2.1: Custom image
- 7.2.1.1: Introduction
- 7.2.1.2: Configuration
- 7.2.1.3: Samples
- 7.2.2: Kubernetes object transformation
- 7.2.2.1: Introduction
- 7.2.2.2: Configuration
- 7.2.3: Run synchronization
- 7.2.3.1: Introduction
- 7.2.3.2: Configuration
- 7.2.3.3: API Reference
- 8: Tutorials
- 8.1: Active-active Kubernetes architecture
- 8.2: Active-passive Kubernetes architecture
- 8.3: Synchronize Zookeeper clusters
- 9: API Reference
1 - Getting started
1.1 - Intro
Astronetes Resiliency Operator is a Kubernetes operator that improves the resiliency of cloud native platforms. It acts as the orchestrator that setup and manages the resiliency of Cloud Native platforms, automating processes and synchronizing data and configurations across multiple technologies.
Astronetes Resiliency Operator helps you to accomplish the following:
- Enable active-active architectures for cloud native platforms
- Automate Disaster Recovery plans for cloud native platforms
Use cases
Active-Active architectures
Active-Active architectures are a proven approach to ensure the required resiliency for mission cricital applications. It protects the application from an outage caused by both technical and operational failures in the platform and its dependencies.
Astronetes Resiliency Operator empowers organizations to deploy and maintain applications across multiple clusters or regions, ensuring maximum uptime and seamless user experiences even during failures or maintenance events.
Disaster Recovery
Business continuity refers to the ability that a particular business can overcome potentially disruptive events with minimal impact in its operations. This no small ordeal requires the definition, implementation of plans, processes and systems while involving complete collaboration and synchronization between multiple actors and departments.
This collection of assets and processes compose the company’s Disaster Recovery. Its goal is to reduce the downtime and data loss in the case of a catastrophic, unforeseen situation. Disaster Recovery needs answer two questions:
- How much data can we lose? - Recovery Point Objective (RPO)
- How long can we take to recover the system? - Recovery Time Objective (RTO)
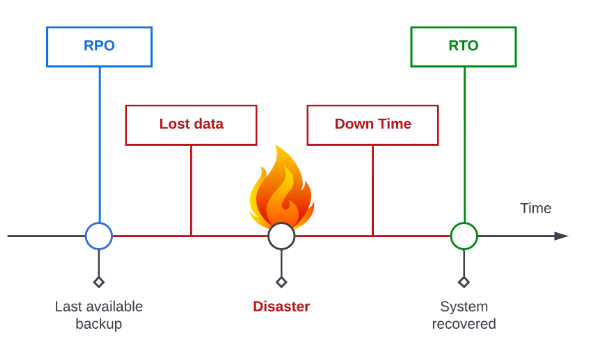
Resiliency Operator provides a solution to improve the business continuity of Cloud Native Platforms by offering a tool that improves resiliency that is transparent in day-to-day operations while having minimal impact in technical maintenance.
Depending on the organisation, system and project necessities resiliency can be improved with a combination of real time synchronization across two or more instances and with a backup and restore strategy. Resiliency Operator implements both methods of data replication across multiple technologies and allows for flexibility on where and how is the information stored.
Business Continuity plans often include complex tests to validate backups content and that they can be restored at any time. To help with these requirements Resiliency Operator includes monitorization systems so that operational teams can make sure that the data is being correctly synchronized and its state in destination.
1.2 - Release notes
v1.3.5
Released: 8 November 2024
Improvements:
- Improved Synchronizations observability providing more details about write operations.
Fixes:
- Fixed kubernetes-to-bucket synchronization plugin whithout using cache
Manifests
Kubernetes:
- crds-kubernetes.yaml
- operator-kubernetes.yaml
- dashboard-assets.json
- dashboard-assets.yaml
- dashboard-synchronizations.json
- dashboard-synchronizations.yaml
OpenShift:
- alert-rules-resiliency-operator.yaml
- crds-openshift.yaml
- operator-openshift.yaml
- dashboard-assets.json
- dashboard-assets.yaml
- dashboard-synchronizations.json
- dashboard-synchronizations.yaml
v1.3.4
Released: 23 October 2024
Improvements:
- Add option to run synchronizations without cache
- Add option to show a log if an object is already in sync during the synchronization process
- Add option to show a log if an object have beed adapted for the destination during the synchronization process
- Add annotations in Kubernetes objects written in synchronizations
- Auto fix OpenShift ImageStreams that references namespaces that don’t exist
- Improved memory management in Kubernetes assets
- Improved zookeeper replication logs showing if a node have been created or updated
- Updated default zookeeper timeout to 5 minutes.
Fixes:
- Many fixes in deployment manifests
- Fixed ServiceAccounts updates
- Fixed status update for SynchronizationPlans
Manifests
Kubernetes:
- crds-kubernetes.yaml
- operator-kubernetes.yaml
- dashboard-assets.json
- dashboard-assets.yaml
- dashboard-synchronizations.json
- dashboard-synchronizations.yaml
OpenShift:
- alert-rules-resiliency-operator.yaml
- crds-openshift.yaml
- operator-openshift.yaml
- dashboard-assets.json
- dashboard-assets.yaml
- dashboard-synchronizations.json
- dashboard-synchronizations.yaml
v1.3.3
Released: 17 September 2024
Improvements:
- Improved plugins start time
Fixes:
- Set synchronization namespace in
astronetes_total_synchronized_objectsmetric - Add webook configuration in deployment manifests
- Fix controllers roles in deployment manifests
- Fix JSONPatch transformations options
Manifests
Kubernetes:
- crds-kubernetes.yaml
- operator-kubernetes.yaml
- dashboard-assets.json
- dashboard-assets.yaml
- dashboard-synchronizations.json
- dashboard-synchronizations.yaml
OpenShift:
- crds-openshift.yaml
- operator-openshift.yaml
- dashboard-assets.json
- dashboard-assets.yaml
- dashboard-synchronizations.json
- dashboard-synchronizations.yaml
v1.3.2
Released: 13 September 2024
Improvements:
- Improved metrics and updated Grafana Dashboard
Manifests
Kubernetes:
- crds-kubernetes.yaml
- operator-kubernetes.yaml
- dashboard-assets.json
- dashboard-assets.yaml
- dashboard-synchronizations.json
- dashboard-synchronizations.yaml
OpenShift:
- crds-openshift.yaml
- operator-openshift.yaml
- dashboard-assets.json
- dashboard-assets.yaml
- dashboard-synchronizations.json
- dashboard-synchronizations.yaml
v1.3.1
Released: 12 September 2024
Improvements:
- Improved plugin configuration validation
- Reduced memory used by synchronizations
- Exposed synchronization Namespace in metrics
Fixes:
- Fixed skipping delete errors in JSONPatch transformations
Manifests
Kubernetes:
- crds-kubernetes.yaml
- operator-kubernetes.yaml
- dashboard-assets.json
- dashboard-assets.yaml
- dashboard-synchronizations.json
- dashboard-synchronizations.yaml
OpenShift:
- crds-openshift.yaml
- operator-openshift.yaml
- dashboard-assets.json
- dashboard-assets.yaml
- dashboard-synchronizations.json
- dashboard-synchronizations.yaml
v1.3.0
Released: 9 September 2024
New features:
- Native support for Google Cloud Storage
- Support synchronizations from Kubernetes to Bucket
- Support synchronizations from Bucket to Kubernetes
- Customize synchronizations with DryRun, ForceSync and ForcePrune options
- Filter objects by namespace name in Kubernetes synchronizations
- Export metrics to inform about Assets status
- Export metrics to inform about synchronizations status
- Export metrics to inform about write operations
Improvements:
- Improved performance in LiveSynchronization from Kubernetes to Kubernetes
- Simplified Kubernetes object selectors in synchronizations
- Reduced amount of internal logs
Manifests
Kubernetes:
OpenShift:
2 - Architecture
2.1 - Overview
Resiliency Operator acts as the orchestrator that setup and manages the resiliency of Cloud Native platforms, automating processes and synchronizing data and configurations across multiple technologies.
It is built with a set of plugins that enables to integrate many technologies and managed services in the resiliency framework.
Key concepts
Assets
Platforms, technologies and services can be linked to the Resiliency Operator to be included in the resiliency framewor, like Kubernetes clusters and databases.
Synchronizations
The synchronization of data and configurations can be configured according to the platform requirements.
| Synchronization Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Synchronization | Synchronize data and configurations only once. |
| SynchronizationPlan | Synchronize data and configurations based on a scheduled period. |
| LiveSynchronization | Real-time synchronization of data and configurations. |
Automation
The Resiliency Operator allows the automation of tasks to be executed when an incident or a disaster occurs.
2.2 - Components
Astronetes Resiliency Operator is software that can be deployed on Kubernetes based clusters. It is composed by a set of controllers that automate and orchestrate the resiliency of Cloud Native platforms.
Operator
| Controllers | Description |
|---|---|
| Bucket | Orchestrate the Bucket obejcts. |
| Database | Orchestrate the Database obejcts. |
| Kubernetes Cluster | Orchestrate the KubernetesCluster obejcts. |
| Live Synchronization | Orchestrate the LiveSynchronization obejcts. |
| Synchronization Plan | Orchestrate the SynchronizationPlan obejcts. |
| Synchronization | Orchestrate the Synchronization obejcts. |
| Task Run | Orchestrate the TaskRun obejcts. |
| Task | Orchestrate the Task obejcts. |
2.3 - Observability
Astronete provides monitoring capabilities by exposing various performance and operational metrics. These metrics allow to gain insight into the system’s health, performance, and behavior, ensuring that you can take proactive measures to maintain system stability.
Metrics
The metrics are exposed in Prometheus format, which is a widely-adopted open-source standard for monitoring. This format enables seamless integration with Prometheus-based monitoring solutions.
Assets by status
The status of each asset managed by the operator: KubernetesClusters, Buckets and Databases.
Prometheus metric: astronetes_asset_status.
Status values: Ready, Progressing, Terminating, Unknown or Failed.
Synchronizations by status
The status of each synchronization object: Synchronization, SynchronizationPlan and LiveSynchronization.
Prometheus metric: astronetes_synchronization_status.
Status values: Ready, Progressing, Terminating, Unknown or Failed.
Total synchronized objects by status
The count of synchronized objects by status.
Prometheus metric: astronetes_total_synchronized_objects.
Status values: Sync, OutOfSync or Unknown.
Alerts
Based on the exposed metrics, alerting can be configured using the widely-adopted open-source standard PrometheusRules. This format enables seamless integration with Prometheus-based monitoring solutions.
Platform alerts
The following alerts reports a possible issue with the platform.
| Alert Name | Description | Severity | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| AssetFailure | At least one asset is failing | critical | 5 minutes |
| SynchronizationFailure | At least one synchronization is failing | critical | 5 minutes |
Applications alerts
The following alerts reports a possible issue with the objects configured to be synchronized. Those alerts are usually related to applications issues.
| Alert Name | Description | Severity | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| SynchronizationNotInSync | There are synchronizations items out of sync | warning | 1 hour |
| WriteOperationsFailed | One or more write operations failed | warning | 1 hour |
2.4 - Audit
Auditing and version control is an important step when configuring resources. Knowing when a change was made and the account that applied it can be determinative in an ongoing investigation to solve an issue or a configuration mismanagement.
Audit annotations
The following annotation are attached to every resource that belongs to Resiliency Operator Custom Resources:
apiVersion: automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: LiveSynchronization
metadata:
annotations:
audit.astronetes.io/last-update-time: "<date>" # Time at which the last update was applied.
audit.astronetes.io/last-update-user-uid: "<uid-hash>" # Hash representing the Unique Identifier of the user that applied the change.
audit.astronetes.io/last-update-username: "<username>" # Human readable name of the user that applied the change.
Example:
apiVersion: automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: LiveSynchronization
metadata:
annotations:
audit.astronetes.io/last-update-time: "2024-02-09T14:05:30.67520525Z"
audit.astronetes.io/last-update-user-uid: "b3fd2a87-0547-4ff7-a49f-cce903cc2b61"
audit.astronetes.io/last-update-username: system:serviceaccount:preproduction:microservice1
Fields are updated only when a change to the fields .spec, .labels or .annotations are detected. Status modifications by the operator are not recorded.
3 - Installation
3.1 - Preparing to install
Prerequisites
- Get familiarized with the architecture reading this section.
- The Secret provided by AstroKube to access the Image Registry.
- The Secret provided by AstroKube with the license key.
Cluster requiremenets
Supported platforms
Astronetes Resiliency Operator is vendor agnostic meaning that any Kubernetes distribution such as Google Kubernetes Engine, Azure Kubernetes Service, OpenShift or self-managed bare metal installations can run it.
This is the certified compatibility matrix:
| Platform | Min Version | Max Version |
|---|---|---|
| AKS | 1.24 | 1.29 |
| EKS | 1.24 | 1.28 |
| GKE | 1.24 | 1.28 |
| OpenShift Container Platform | 4.11 | 4.14 |
Permissions
To install the Resiliency Operator on a cluster, you need to have Cluster Admin permissions in that cluster.
The Resiliency Operator needs read access to the assets being protected and read/write access to the backup assets. Refer to plugin documentation for details.
Kubernetes requirements
Software
- Official kubernetes.io client CLI kubectl.
Networking
- Allow traffic to the Image Registry quay.io/astrokube using the mechanism provided by the chosen distribution.
OpenShift requirements
Software
- Official OpenShift client CLI.
Networking
- Add quay.io/astrokube to the allowed registries in the Image configuration.
apiVersion: config.openshift.io/v1
kind: Image
metadata:
...
spec:
registrySources:
allowedRegistries:
...
- quay.io/astrokube
3.2 - Installing on Kubernetes
Prerequisites
- Review the documenation about preparing for the installation.
- The
pull-secret.yamlSecret provided by AstroKube to access the Image Registry. - The license-key.yaml` Secret provided by AstroKube with the license key.
- Install cert-manager and prometheus in cluster
Process
1. Create Namespace
Create the Namespace where the operator will be installed:
oc create namespace resiliency-operator
2. Setup registry credentials
Create the Secret that stores the credentials to the AstroKube image registry:
oc -n resiliency-operator create -f pull-secret.yaml
3. Setup license key
Create the Secret that stores the license key:
oc -n resiliency-operator create -f license-key.yaml
4. Install the operator
Install the CRDs:
oc apply -f https://astronetes.io/deploy/resiliency-operator/v1.3.5/crds-kubernetes.yaml
Install the operator:
oc -n resiliency-operator apply -f https://astronetes.io/deploy/resiliency-operator/v1.3.5/operator-kubernetes.yaml
3.3 - Installing on OpenShift
Prerequisites
- Review the documenation about preparing for the installation.
- The
pull-secret.yamlSecret provided by AstroKube to access the Image Registry. - The license-key.yaml` Secret provided by AstroKube with the license key.
Process
1. Create Namespace
Create the Namespace where the operator will be installed:
oc create namespace resiliency-operator
2. Setup registry credentials
Create the Secret that stores the credentials to the AstroKube image registry:
oc -n resiliency-operator create -f pull-secret.yaml
3. Setup license key
Create the Secret that stores the license key:
oc -n resiliency-operator create -f license-key.yaml
4. Install the operator
Install the CRDs:
oc apply -f https://astronetes.io/deploy/resiliency-operator/v1.3.5/crds-openshift.yaml
Install the operator:
oc -n resiliency-operator apply -f https://astronetes.io/deploy/resiliency-operator/v1.3.5/operator-openshift.yaml
3.4 - Uninstalling on Kubernetes
Process
1. Delete Operator objects
Delete the synchronizations from the cluster:
oc delete livesynchronizations.automation.astronetes.io -A --all
oc delete synchronizationplans.automation.astronetes.io -A --all
oc delete synchronizations.automation.astronetes.io -A --all
Delete the assets from the cluster:
oc delete buckets.assets.astronetes.io -A --all
oc delete databases.assets.astronetes.io -A --all
oc delete kubernetesclusters.assets.astronetes.io -A --all
2. Remove the operator
Delete the operator:
oc -n resiliency-operator delete -f https://astronetes.io/deploy/resiliency-operator/v1.3.5/operator-kubernetes.yaml
Delete the CRDs:
oc delete -f https://astronetes.io/deploy/resiliency-operator/v1.3.5/crds-kubernetes.yaml
3. Remove registry credentials
Delete the Secret that stores the credentials to the AstroKube image registry:
oc -n resiliency-operator delete -f pull-secret.yaml
4. Remove license key
Delete the Secret that stores the license key:
oc -n resiliency-operator delete -f license-key.yaml
3.5 - Uninstalling on OpenShift
Process
1. Delete Operator objects
Delete the synchronizations from the cluster:
oc delete livesynchronizations.automation.astronetes.io -A --all
oc delete synchronizationplans.automation.astronetes.io -A --all
oc delete synchronizations.automation.astronetes.io -A --all
Delete the assets from the cluster:
oc delete buckets.assets.astronetes.io -A --all
oc delete databases.assets.astronetes.io -A --all
oc delete kubernetesclusters.assets.astronetes.io -A --all
2. Remove the operator
Delete the operator:
oc -n resiliency-operator delete -f https://astronetes.io/deploy/resiliency-operator/v1.3.5/operator-openshift.yaml
Delete the CRDs:
oc delete -f https://astronetes.io/deploy/resiliency-operator/v1.3.5/crds-openshift.yaml
3. Remove registry credentials
Delete the Secret that stores the credentials to the AstroKube image registry:
oc -n resiliency-operator delete -f pull-secret.yaml
4. Remove license key
Delete the Secret that stores the license key:
oc -n resiliency-operator delete -f license-key.yaml
4 - Configure
4.1 - Integrating with Grafana
Introduction
The Resiliency Operator exports metrics in Prometheus format that can be visualized using custom Grafana dashboards.
Prerequisites
- Prometheus installed in the Kubernetes cluster
- Grafana configured to access the Prometheus
Process
1. Import dashboard for Assets
Access to Grafana and navigate to Home > Dashboards > Import.
Set the dashboard URL to https://astronetes.io/deploy/resiliency-operator/v1.3.5/grafana-dashboard-assets.json and click Load.
Configure the import and click con Import button to complete the process.
2. Import dashboard for Synchronizations
Access to Grafana and navigate to Home > Dashboards > Import.
Set the dashboard URL to https://astronetes.io/deploy/resiliency-operator/v1.3.5/grafana-dashboard-synchronizations.json and click Load.
Configure the import and click con Import button to complete the process.
4.2 - Integrating with Grafana Operator
Introduction
The Resiliency Operator exports metrics in Prometheus format that can be visualized using custom Grafana dashboards.
Prerequisites
- Prometheus installed in the Kubernetes cluster
- Grafana Operator installed in the cluster and configured to access the Prometheus
Process
1. Create the GrafanaDashboard for Assets
Create the GrafanaDashboard for Assets from the release manifests:
kubectl apply -f https://astronetes.io/deploy/resiliency-operator/v1.3.5/dashboard-assets.yaml
2. Create the GrafanaDashboard for Synchronizations
Create the GrafanaDashboard for Synchronizations from the release manifests:
kubectl apply -f https://astronetes.io/deploy/resiliency-operator/v1.3.5/dashboard-synchronizations.yaml
4.3 - Integrating with OpenShift Alerting
Introduction
OpenShift allows the creation of alerts based on Prometheus metrics to provide additional information about the functioning and status of Astronetes operator.
Prerequisites
- Access Requirement: cluster-admin access to the OpenShift cluster
Configure alerts
Two types of alerts are provided for managing the operator’s integration within the cluster and for monitoring the synchronization
Platform alerts
Metrics defined to assess the functionality of the integration between the product and the assets
Applying these rules:
oc apply -f https://astronetes.io/deploy/resiliency-operator/v1.3.5/alert-rules-resiliency-operator.yaml
Synchronization alerts
Metrics are employed to assess the status of synchronized objects.
For configuring this rule its necesary to follow these steps:
- Create this PrometheusRule manifest:
apiVersion: monitoring.coreos.com/v1
kind: PrometheusRule
metadata:
name: failed-synchronize-items
namespace: <your-synchronization-namespace>
spec:
groups:
- name: synchronization-alerts
rules:
- alert: SynchronizationNotInSync
annotations:
summary: "There are synchronization items not in sync."
description: "Synchronization {{ $labels.synchronizationName }} is out of sync in namespace {{ $labels.synchronizationNamespace }}"
expr: astronetes_total_synchronized_objects{objectStatus!="Sync"} > 0
for: 1h
labels:
severity: warning
- alert: WriteOperationsFailed
annotations:
summary: "There are one or more write operations failed"
description: "Synchronization {{ $labels.synchronizationName }} failed write operator in namespace {{ $labels.synchronizationNamespace }}"
expr: astronetes_total_write_operations{writeStatus="failed"} > 0
for: 1h
labels:
severity: warning
Edit namespace: Use the namespace where synchronizes are deployed
Applying this rule:
kubectl apply -f <path-to-your-modified-yaml-file>.yaml
How to configure custom alerts
Prometheus provides a powerful set of metrics that can be used to monitor the status of your cluster and the functionality of your operator by creating customized alert rules.
The PrometheusRule should be created in the same namespace as the process that generates these metrics to ensure proper functionality and visibility.
Here is an example of a PrometheusRule YAML file:
apiVersion: monitoring.coreos.com/v1
kind: PrometheusRule
metadata:
name: <alert-name>
namespace: <namespace>
spec:
groups:
- name: <group-name>
rules:
- alert: <alert-rule-name>
annotations:
description: <description>
summary: <summary>
expr: <expresion>
for: <duration>
labels:
severity: <severity-level>
Field Value Descriptions
In the PrometheusRule YAML file, several fields are essential for defining your alerting rules. Below is a table describing the values that can be used for each field:
| Field | Description | Example Values |
|---|---|---|
| alert | Specifies the name of the alert that will be triggered. It should be descriptive. | AssetFailure, HighCPUUsage, MemoryThresholdExceeded |
| for | Defines the duration for which the condition must be true before the alert triggers. | 5m, 1h, 30s |
| severity | Indicates the criticality of the alert. Helps prioritize alerts. | critical, warning, info |
| expr | The Prometheus expression (in PromQL) that determines the alerting condition based on metrics. | sum(rate(http_requests_total[5m])) > 100, node_memory_usage > 90 |
Apply to the cluster
Create new prometheus rule in the cluster:
oc apply -f <path-to-your-prometheus-rule-file>.yaml
Checking alerts
1. Access OpenShift Web Console:
- Open your browser and go to the OpenShift web console URL.
- Log in with your credentials.
2. Navigate to Observe:
- In the OpenShift console, go to the Observe section from the main menu.
- In the Alerts tab, you’ll find a list of active and silenced alerts.
- Check for any alerts triggered based on the custom rules you can create in Prometheus.
- Also you can see the entire list of alerting rules configurated.
3. Filter Custom Alerts:
- To filter the custom alerts, use the source field and set its value to user. This will display only the alerts that were generated based on user-defined rules. Check openshift docs about filtering.
4.4 - Update license key
There is no need to reinstall the operator when updating the license key.
Process
1. Update the license key
Update the Kubernetes Secret that stores the license key with the new license:
kubectl -n resiliency-operator apply -f new-license-key.yaml
oc -n resiliency-operator apply -f new-license-key.yaml
2. Restart the Resiliency Operator
Restart the Resiliency Operator Deployment to apply the new license:
kubectl -n resiliency-operator rollout restart deployment resiliency-operator-bucket-controller
kubectl -n resiliency-operator rollout restart deployment resiliency-operator-database-controller
kubectl -n resiliency-operator rollout restart deployment resiliency-operator-kubernetescluster-controller
kubectl -n resiliency-operator rollout restart deployment resiliency-operator-livesynchronization-controller
kubectl -n resiliency-operator rollout restart deployment resiliency-operator-synchronization-controller
kubectl -n resiliency-operator rollout restart deployment resiliency-operator-synchronizationplan-controller
kubectl -n resiliency-operator rollout restart deployment resiliency-operator-task-controller
kubectl -n resiliency-operator rollout restart deployment resiliency-operator-taskrun-controller
oc -n resiliency-operator rollout restart deployment resiliency-operator-bucket-controller
oc -n resiliency-operator rollout restart deployment resiliency-operator-database-controller
oc -n resiliency-operator rollout restart deployment resiliency-operator-kubernetescluster-controller
oc -n resiliency-operator rollout restart deployment resiliency-operator-livesynchronization-controller
oc -n resiliency-operator rollout restart deployment resiliency-operator-synchronization-controller
oc -n resiliency-operator rollout restart deployment resiliency-operator-synchronizationplan-controller
oc -n resiliency-operator rollout restart deployment resiliency-operator-task-controller
oc -n resiliency-operator rollout restart deployment resiliency-operator-taskrun-controller
3. Wait for the Pods restart
Wait a couple of minutes until all the Resiliency Operator Pods are restarted with the new license.
kubectl -n resiliency-operator wait --for=condition=available deployment/resiliency-operator-bucket-controller
kubectl -n resiliency-operator wait --for=condition=available deployment/resiliency-operator-database-controller
kubectl -n resiliency-operator wait --for=condition=available deployment/resiliency-operator-kubernetescluster-controller
kubectl -n resiliency-operator wait --for=condition=available deployment/resiliency-operator-livesynchronization-controller
kubectl -n resiliency-operator wait --for=condition=available deployment/resiliency-operator-synchronization-controller
kubectl -n resiliency-operator wait --for=condition=available deployment/resiliency-operator-synchronizationplan-controller
kubectl -n resiliency-operator wait --for=condition=available deployment/resiliency-operator-task-controller
kubectl -n resiliency-operator wait --for=condition=available deployment/resiliency-operator-taskrun-controller
oc -n resiliency-operator wait --for=condition=available deployment/resiliency-operator-bucket-controller
oc -n resiliency-operator wait --for=condition=available deployment/resiliency-operator-database-controller
oc -n resiliency-operator wait --for=condition=available deployment/resiliency-operator-kubernetescluster-controller
oc -n resiliency-operator wait --for=condition=available deployment/resiliency-operator-livesynchronization-controller
oc -n resiliency-operator wait --for=condition=available deployment/resiliency-operator-synchronization-controller
oc -n resiliency-operator wait --for=condition=available deployment/resiliency-operator-synchronizationplan-controller
oc -n resiliency-operator wait --for=condition=available deployment/resiliency-operator-task-controller
oc -n resiliency-operator wait --for=condition=available deployment/resiliency-operator-taskrun-controller
5 - Assets
Platforms, technologies and services can be linked to the Resiliency Operator to enable process automation and data synchronization.
5.1 - Introduction
An Asset is any kind of platform, technology or service that can be imported into the operator to improve its resiliency. Assets can include Kubernetes clusters and databases.
Asset types
Kubernetes Cluster
While the system is designed to be compatible with all kinds of Kubernetes clusters, official support and testing are limited to a specific list of Kubernetes distributions. This ensures that the synchronization process is reliable, consistent, and well-supported.
This is the list of officially supported Kubernetes distributions:
| Distribution | Versions |
|---|---|
| OpenShift Container Platform | 4.12+ |
| Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) | 1.28+ |
| Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS) | 1.26+ |
| Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) | 1.28+ |
Buckets
Public cloud storage containers for objects stored in simple storage service.
Databases
| Database | Versions |
|---|---|
| Zookeeper | 3.6+ |
5.2 - Buckets
5.2.1 - Import GCP Cloud Storage
Buckets hosted in Cloud Storage can be imported as GCP CLoud Storage.
Requirements
The Bucket properties:
- Bucket name
- GCP project ID
The credentials to access the bucket:
- The ServiceAccount key
Process
1. Create the Secret
Store the following file as secret.yaml and substitute the template parameters with real ones.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: bucket-credentials
stringData:
application_default_credentials.json: '{...}'
Then create the Secret with the following command:
kubectl -n <namespace_name> apply -f secret.yaml
2. Create the object
Store the following file as bucket.yaml and substitute the template parameters with real ones.
apiVersion: assets.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: Bucket
metadata:
name: <name>
namespace: <namespace>
spec:
gcpCloudStorage:
name: <gcp-project-name>
projectID: <gcp-project-id>
secretName: gcp-bucket
Deploy the resource with the following command:
kubectl create -f bucket.yaml
5.2.2 - Import generic bucket
Buckets that support AWS S3 protocol (like Minio), can be imported as a generic bucket.
Requirements
The Bucket properties:
- Bucket endpoint
- Bucket name
The credentials to access the bucket:
- The access key ID
- The ssecret access key
Process
1. Create the Secret
Store the following file as secret.yaml and substitute the template parameters with real ones.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: bucket-credentials
stringData:
accessKeyID: <access_key_id>
secretAccessKey: <secret_access_key>
Then create the Secret with the following command:
kubectl -n <namespace_name> apply -f secret.yaml
2. Create the Bucket
Store the following file as bucket.yaml and substitute the template parameters with real ones.
apiVersion: assets.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: Bucket
metadata:
name: <name>
namespace: <namespace>
spec:
generic:
endpoint: mybucket.example.com
name: <bucket_name>
useSSL: true
secretName: bucket-credentials
Deploy the resource with the following command:
kubectl create -f bucket.yaml
5.2.3 - Configurations
Intro
The import of each Bucket can be configured with some specific parameters using the .spec.config attribute.
apiVersion: assets.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: Bucket
metadata:
name: my-bucket
spec:
...
config: {}
Limit assigned resources
For each Bucket imported, a new Pod is deployed inside the same Namespace. The limit and requests resources can be set using the .spec.config.resources field.
Example:
apiVersion: assets.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: Bucket
metadata:
name: my-cluster
spec:
...
config:
resources:
requests:
cpu: 1
memory: 2Gi
limits:
cpu: 2
memory: 2Gi
Filter the watched resources
By default, the operator will watch all the files in the bucket. You can filter the list of path to be watched by configuring the .spec.config.paths field.
Example:
apiVersion: assets.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: Bucket
metadata:
name: my-bucket
spec:
...
config:
paths:
- example1/
Concurrency
The concurrency parameter can be used to improve the peformance of the operator on listening the changes that happens in the Bucket.
Example:
apiVersion: assets.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: Bucket
metadata:
name: my-cluster
spec:
...
config:
concurrency: 200
5.2.4 - API Reference
Config
Customize the integration with a Bucket
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
concurrency | Concurrent processes to be executed to improve performance | int | false |
interval | Interval of which | string | false |
logLevel | Log level to be used by the related Pod | string | false |
observability | Observability configuration | ObservabilityConfig | false |
paths | Filter the list of paths to be listened | []string | false |
resources | Resources to be assigned to the synchronization Pod | ResourceRequirements | false |
ObservabilityConfig
Configure the synchronization process observability using Prometheus ServiceMonitor
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
enabled | Enable the Observability with a Prometheus ServiceMonitor | bool | false |
interval | Configure the interval in the ServiceMonitor that Prometheus will use to scrape metrics | Duration | false |
Duration
Duration is a wrapper around time.Duration which supports correct marshaling to YAML and JSON. In particular, it marshals into strings, which can be used as map keys in json.
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|
5.3 - Databases
5.3.1 - Import Zookeeper
Zookeeper clusters can be imported with the Database resource.
Requirements
- The Zookeeper server hosts
Process
1. Create the object
Define the Database resource with the following YAML, and save it as database.yaml:
apiVersion: assets.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: Database
metadata:
name: zookeeper
spec:
zookeeper:
client:
servers:
- 172.18.0.4:30181
- 172.18.0.5:30181
- 172.18.0.6:30181
Deploy the resource with the following command:
kubectl create -f database.yaml
5.4 - Kubernetes Clusters
5.4.1 - Import
Any kind of KubernetesCluster can be imported in the operator. Credentials are stored in Kubernetes secrets from which the KubernetesCluster collection access to connect to the clusters.
Once you have imported the KubernetesCluster, all the resources in the cluster that can be watched, will be read by the operator.
Requirements
- The kubeconfig file to access the cluster
Process
1. Create the Secret
Get the kubeconfig file that can be used to access the cluster, and save it as kubeconfig.yaml.
Then create the Secret with the following command:
kubectl create secret generic source --from-file=kubeconfig.yaml=kubeconfig.yaml
2. Create the KubernetesCluster
Define the KubernetesCluster object with the following YAML, and save it as cluster.yaml:
apiVersion: assets.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: KubernetesCluster
metadata:
name: cluster-1
spec:
secretName: <secret_name>
Deploy the resource with the following command:
kubectl create -f cluster.yaml
5.4.2 - Configurations
Intro
The import of each KubernetesCluster can be configured with some specific parameters using the .spec.config attribute.
apiVersion: assets.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: KubernetesCluster
metadata:
name: my-cluster
spec:
secretName: my-cluster-secret
config: {}
Limit assigned resources
For each Kubernetes Cluster imported, a new Pod is deployed inside the same Namespace. The limit and requestsresources can be set using the.spec.config.resources` field.
Example:
apiVersion: assets.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: KubernetesCluster
metadata:
name: my-cluster
spec:
secretName: my-cluster-secret
config:
resources:
requests:
cpu: 1
memory: 2Gi
limits:
cpu: 2
memory: 2Gi
Filter the watched resources
By default, the operator will watch all the available resources int he cluster that can be watched. You can filter the list of this resources by configuring the .spec.config.selectors field.
Example:
apiVersion: assets.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: KubernetesCluster
metadata:
name: my-cluster
spec:
secretName: my-cluster-secret
config:
selectors:
targets:
- group: ""
version: v1
resources:
- namespaces
- secrets
- configmaps
- serviceaccounts
- resourcequotas
- limitranges
- persistentvolumeclaims
- group: policy
version: v1
resources:
- poddisruptionbudgets
Concurrency
The concurrency parameter can be used to improve the peformance of the operator on listening the changes that happens in the Kubernetes Cluster.
Example:
apiVersion: assets.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: KubernetesCluster
metadata:
name: my-cluster
spec:
secretName: my-cluster-secret
config:
concurrency: 200
5.4.3 - API Reference
Config
Customize the integration with a KubernetesCluster
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
concurrency | Concurrent processes to be executed to improve performance | int | false |
logLevel | Log level to be used by the related Pod | string | false |
observability | Observability configuration | ObservabilityConfig | false |
resources | Resources to be assigned to the synchronization Pod | ResourceRequirements | false |
selectors | Filter the list of resources to be listened | KubernetesClusterSelectors | false |
ObservabilityConfig
Configure the synchronization process observability using Prometheus ServiceMonitor
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
enabled | Enable the Observability with a Prometheus ServiceMonitor | bool | false |
interval | Configure the interval in the ServiceMonitor that Prometheus will use to scrape metrics | Duration | false |
Duration
Duration is a wrapper around time.Duration which supports correct marshaling to YAML and JSON. In particular, it marshals into strings, which can be used as map keys in json.
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|
KubernetesClusterSelectors
Filter the Kubernetes objects that should be read from the cluster
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
objectSelector | Rules to filter Kubernetes objects by ObjectSelector | ObjectSelector | false |
namespaceSelector | Rules to filter Kubernetes objects by NamespaceSelector | NamespaceSelector | false |
targets | Kuberentes resourcs to be usedr | []GroupVersionResources | false |
ObjectSelector
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
nameSelector | Filter objects by their name | NameSelector | false |
labelSelector | Filter objects by their labels | LabelSelector | false |
NameSelector
Select object by their name
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
includeRegex | Include names that matches at least one regex | []string | false |
excludeRegex | Exlcude names that matches at least one regex | []string | false |
LabelSelector
A label selector is a label query over a set of resources. The result of matchLabels and matchExpressions are ANDed. An empty label selector matches all objects. A null label selector matches no objects. +structType=atomic
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
matchLabels | matchLabels is a map of {key,value} pairs. A single {key,value} in the matchLabelsmap is equivalent to an element of matchExpressions, whose key field is “key”, theoperator is “In”, and the values array contains only “value”. The requirements are ANDed.+optional | map[string]string | false |
matchExpressions | matchExpressions is a list of label selector requirements. The requirements are ANDed.+optional+listType=atomic | []LabelSelectorRequirement | false |
LabelSelectorRequirement
A label selector requirement is a selector that contains values, a key, and an operator that relates the key and values.
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
key | key is the label key that the selector applies to. | string | false |
operator | operator represents a key’s relationship to a set of values.Valid operators are In, NotIn, Exists and DoesNotExist. | LabelSelectorOperator | false |
values | values is an array of string values. If the operator is In or NotIn,the values array must be non-empty. If the operator is Exists or DoesNotExist,the values array must be empty. This array is replaced during a strategicmerge patch.+optional+listType=atomic | []string | false |
LabelSelectorOperator
A label selector operator is the set of operators that can be used in a selector requirement.
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|
NamespaceSelector
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
nameSelector | Filter Namespaces by their name | NameSelector | false |
labelSelector | Filter Namespaces by their labels | LabelSelector | false |
GroupVersionResources
Select a set of GroupVersionResource
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
group | Kubernetes resource group. Example: apps | string | false |
version | Kubernetes resource version. Example: v1 | string | false |
resources | Kubernetes resource names. Example: deployments | []string | false |
6 - Synchronization
6.1 - Introduction
Synchronization is a critical process that enables the replication of data and configurations across different platform assets. This ensures consistency, integrity and improve the platform resiliency.
Key concepts
Source and destination
Each synchronization has at least two assets:
- Source: the original location or system from which data and configurations are retrived.
- Destination: the destination location or system where data and configurations are applied or updated.
Synchronization periodicity
There are three distinct types of synchronization processes designed to meet different operational needs: Synchronization, SynchronizationPlan, and LiveSynchronization.
Synchronization
The Synchronization process is designed to run once, making it ideal for one-time data alignment tasks or initial setup processes. This type of synchronization is useful when a system or component needs to be brought up-to-date with the latest data and configurations from another source without ongoing updates.
The synchronization process follows these rules:
- Object exists in Source: If a matching object exists in the source asset, it will be synchronized to the destination asset.
- Object only in Destination: If a matching object exists only in the destination asset, it will be removed from the destination asset.
SynchronizationPlan
The SynchronizationPlan process operates similarly to a cron job, allowing synchronization tasks to be scheduled at regular intervals. This type is ideal for systems that require periodic updates to ensure data and configuration consistency over time without the need for real-time accuracy.
LiveSynchronization
LiveSynchronization provides real-time synchronization, continuously monitoring and updating data and configurations as changes occur. This type of synchronization is essential for environments where immediate consistency and up-to-date information are crucial.
The synchronization process follows these rules:
- Object Creation/Update in Source: If a matching object is created or updated in the source asset, it will be synchronized to the destination asset.
- Object Deletion in Source: If a matching object is deleted in the source asset, the corresponding object will be deleted in the destination asset.
- Object Creation/Update in Destination: If a matching object is created or updated in the destination asset, it will be synchronized from the source asset.
- Object Deletion in Source: If a matching object is deleted in the source asset, the corresponding object will be deleted in the destination asset.
- Object Only in Destination: If a matching object exists only in the destination asset, it will be removed from the destination asset.
Resume
| Periodicity | Description |
|---|---|
| Synchronization | Synchronize data and configurations only once. |
| SynchronizationPlan | Synchronize data and configurations based on a scheduled period. |
| LiveSynchronization | Real-time synchronization of data and configurations. |
Prerequisites
Before initiating the Synchronization process, ensure the following prerequisites are met:
- Both source and destiation systems have been defined as Asset.
- There is a network connectivity between the assets and the operator.
6.2 - Bucket to Kubernetes
6.2.1 - Introduction
Bucket files can be synchronized in a Kubernetes cluster as Kubernetes objects using the bucket-to-kubernetes plugin.
Synchronization process
Special rules
There are no special rules for this synchronization plugin.
Blacklisted objects
There are some Kubernetes objects that are blacklisted by default and will be ignored by the synchronization process.
This is the list of the blacklisted objects:
- Namespaces which name starts with
kube-oropenshift, an the Namespaceresiliency-operator. - All namespaced objects inside a blacklisted Namespace.
- ConfigMaps named
kube-root-ca.crtoropenshift-service-ca.crt.
Objects path
The files from the bucket will be read as Kubernetes objectsfrom files with the following path: <group>.<version>.<kind>/<object_namespace>.<object_name>.
Examples:
- The Namespace named
testwill be saved in the filecore.v1.Namespace/test. - The Deployment named
app-1deployed in thetestNamespace will be saved in the fileapps.v1.Deployment/test.app-1.
Use cases
Backup restore
Restore your Kubernetes cluster from a Bucket.
Pilot light architecture
Recover from a disaster by running the application saved in the Bucket.
6.2.2 - Configuration
Introduction
The synchronization process can be configured with some specific parameters using the .spec.config attribute.
apiVersion: automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: Synchronization
metadata:
name: example
spec:
plugin: bucket-to-kubernetes
config:
...
Required configuration
Source and destination
The source bucket and the destination cluster can be specified using the .spec.config.sourceName and .spec.config.destinationName properties. Both the KubernetesCluster and the bucket objects should exists in the same Namespace where the synchronization is being created.
Example:
apiVersion: automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: Synchronization
metadata:
name: example
spec:
plugin: bucket-to-kubernetes
config:
sourceName: bucket-1
destinationName: cluster-1
...
Selectors
The resources that should be synchronized can be configured using the .spec.config.selectors property.
Example:
apiVersion: automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: Synchronization
metadata:
name: example
spec:
plugin: bucket-to-kubernetes
config:
...
selectors:
- target:
version: v1
resources:
- namespaces
objectSelector:
labelSelector:
matchLabels:
env: pro
Optional configuration
Global selectors
Global selectors are used to set the default value on all selectors defined in .spec.config.selectors. They can be configured with the .spec.config.globalSelector property.
There are two options allowed, that can be configured at the same time:
namespaceSelector: to set e dafult namespace selector for namespaced resourcesobjectSelector: to set a default object selector for all resources
Example:
apiVersion: automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: Synchronization
metadata:
name: example
spec:
plugin: bucket-to-kubernetes
config:
...
globalSelector:
namespaceSelector:
labelSelector:
matchLabels:
env: pro
objectSelector:
labelSelector:
matchLabels:
env: pro
Path prefix
The Kubernetes objects can be written in a subdirectory of the destination Bucket. The property .spec.config.pathPrefix allows this configuration.
Example:
apiVersion: automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: Synchronization
metadata:
name: example
spec:
plugin: bucket-to-kubernetes
config:
...
pathPrefix: prefix-path
Log level
The log level of the Pod deployed to execute the synchronization, can be configured with the .spec.config.logLevel parameter.
info.
Accepted values: debug, info, warn, error.Example:
apiVersion: automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: Synchronization
metadata:
name: example
spec:
plugin: bucket-to-kubernetes
config:
...
logLevel: warn
Observability
Observability can be enaled using the specific .spec.config.observability parameter. For more information check the Observability page.
Default value:
enabled: false
interval: 60s
Example:
apiVersion: automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: Synchronization
metadata:
name: example
spec:
plugin: bucket-to-kubernetes
config:
...
observability:
enabled: true
interval: 2m
Limit assigned resources
For each synchronization, a new Pod is deployed inside the same Namespace. The limit and requests resources can be set using the .spec.config.resources field.
{}.Example:
apiVersion: automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: Synchronization
metadata:
name: example
spec:
plugin: bucket-to-kubernetes
config:
...
resources:
requests:
cpu: 1
memory: 2Gi
limits:
cpu: 2
memory: 2Gi
Concurrency
The concurrency parameter can be used to improve the peformance of the synchronization process with .spec.config.concurrency`.
100.Example:
apiVersion: automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: Synchronization
metadata:
name: example
spec:
plugin: bucket-to-kubernetes
config:
...
concurrency: 200
Transformations
Objects from the source bucket can be transformed before being synchronized into the destination cluster.
Example:
apiVersion: automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: Synchronization
metadata:
name: example
spec:
plugin: bucket-to-kubernetes
config:
...
transformations:
resources:
- version: v1
resources:
- namespaces
operations:
- jsonpatch:
operations:
- op: add
path: /metadata/labels/test-astrosync
value: ok
API Reference
| Name | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| sourceName | Bucket name | string | yes |
| destinationName | KubernetesCluster name | string | yes |
| selectors | The Kubernetes resources to be syncrhonized | []KubernetesObjectSelector | yes |
| globalSelector | Global selectors to be applied to all selectors | KubernetesGlobalSelector | yes |
6.2.3 - Observability
Introduction
The synchronization process exports many metrics in Prometheus format over HTTP.
Exported metrics
The following metrics are available:
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
astronetes_synchronization_status | The status of each synchronization object. |
astronetes_synchronization_status_total | The count of synchronization objects for each state. |
Requirements
- The
ServiceMonitorCRD from prometheus (servicemonitors.monitoring.coreos.com) must be enabled in the cluster where the operator is running.
Processes
Enable observability
Update the synchronization configuration, setting the paramente .spec.config.observability.enabled to true.
Once enabled the observability, a ServiceMonitor will be created in the same Namespace of the related synchronization.
Disable observability
Update the synchronization configuration, setting the paramente .spec.config.observability.enabled to false.
6.2.4 - API Reference
Config
Configuration for Bucket to Kubernetes synchronization
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
concurrency | Concurrent processes to be executed to improve performance | int | false |
destinationName | KubernetesCluster name where data will be synchronized | string | false |
globalSelector | Overrides selectors properties | KubernetesGlobalSelector | false |
logLevel | Log level to be used by the synchronization Pod | string | false |
observability | Observability configuration | ObservabilityConfig | false |
options | Synchronization options | SynchronizationOptions | false |
pathPrefix | Path prefix to be used to retreive objects in the Bucket | string | false |
resources | Resources to be assigned to the synchronization Pod | ResourceRequirements | false |
selectors | Selectors to filter the Kubernetes resources to be synchronized | []KubernetesObjectSelector | false |
sourceName | Bucket name from where data will be read | string | false |
transformations | Transform Kubernetes objects before to be written to the destination | []Transformations | false |
useCachedData | Use cached data instead of get data from Kubernetes clusters on startup | bool | false |
KubernetesGlobalSelector
Global selector is used to set the default value on all selectors
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
objectSelector | Rules to filter Kubernetes objects by ObjectSelector | ObjectSelector | false |
namespaceSelector | Rules to filter Kubernetes objects by NamespaceSelector | NamespaceSelector | false |
ObjectSelector
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
nameSelector | Filter objects by their name | NameSelector | false |
labelSelector | Filter objects by their labels | LabelSelector | false |
NameSelector
Select object by their name
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
includeRegex | Include names that matches at least one regex | []string | false |
excludeRegex | Exlcude names that matches at least one regex | []string | false |
LabelSelector
A label selector is a label query over a set of resources. The result of matchLabels and matchExpressions are ANDed. An empty label selector matches all objects. A null label selector matches no objects. +structType=atomic
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
matchLabels | matchLabels is a map of {key,value} pairs. A single {key,value} in the matchLabelsmap is equivalent to an element of matchExpressions, whose key field is “key”, theoperator is “In”, and the values array contains only “value”. The requirements are ANDed.+optional | map[string]string | false |
matchExpressions | matchExpressions is a list of label selector requirements. The requirements are ANDed.+optional+listType=atomic | []LabelSelectorRequirement | false |
LabelSelectorRequirement
A label selector requirement is a selector that contains values, a key, and an operator that relates the key and values.
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
key | key is the label key that the selector applies to. | string | false |
operator | operator represents a key’s relationship to a set of values.Valid operators are In, NotIn, Exists and DoesNotExist. | LabelSelectorOperator | false |
values | values is an array of string values. If the operator is In or NotIn,the values array must be non-empty. If the operator is Exists or DoesNotExist,the values array must be empty. This array is replaced during a strategicmerge patch.+optional+listType=atomic | []string | false |
LabelSelectorOperator
A label selector operator is the set of operators that can be used in a selector requirement.
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|
NamespaceSelector
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
nameSelector | Filter Namespaces by their name | NameSelector | false |
labelSelector | Filter Namespaces by their labels | LabelSelector | false |
ObservabilityConfig
Configure the synchronization process observability using Prometheus ServiceMonitor
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
enabled | Enable the Observability with a Prometheus ServiceMonitor | bool | false |
interval | Configure the interval in the ServiceMonitor that Prometheus will use to scrape metrics | Duration | false |
Duration
Duration is a wrapper around time.Duration which supports correct marshaling to YAML and JSON. In particular, it marshals into strings, which can be used as map keys in json.
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|
SynchronizationOptions
Customize the synchronization process with special options
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
dryRun | Simulate the synchronization process but don’t execute the write operations | bool | false |
forceSync | Synchronize object in the destination even if the object exists in the destination and it doesn’t match the configured selectors | bool | false |
forcePrune | Prune object in the destination even if it doesn’t match the configured selectors | bool | false |
showLogIfObjectIsAlreadyInSync | Show a log message if object is already in sync | bool | false |
showLogIfObjectHaveBeenAdapted | Show a log message if object have been adapted for the destination | bool | false |
KubernetesObjectSelector
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
objectSelector | Filter objects by ObjectSelector | ObjectSelector | false |
namespaceSelector | Filter objects by NamespaceSelector | NamespaceSelector | false |
target | Kubernetes resource to be used | GroupVersionResources | false |
GroupVersionResources
Select a set of GroupVersionResource
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
group | Kubernetes resource group. Example: apps | string | false |
version | Kubernetes resource version. Example: v1 | string | false |
resources | Kubernetes resource names. Example: deployments | []string | false |
Transformations
Transformations is a list of operations to modifiy the Kubernetes objects matching the given selectors
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
resources | Select the objects to be transfomred by their resource type | []GroupVersionResources | false |
namespaceSelector | Filter the objects to be transformed by NamespaceSelector | NamespaceSelector | false |
objectSelector | Filter the objects to be transformed by ObjectSelector | ObjectSelector | false |
operations | Operations to be executed to transform the objects | []TransformationOperation | false |
TransformationOperation
The operation to execute to transform the objects
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
jsonpatch | JSONPatch operation | OperationJSONPatch | false |
OperationJSONPatch
The JSONPatch operation
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
skipIfNotFoundOnDelete | Skip if not found on delete | bool | false |
operations | List of operations to be executed | []JSONPatchOperation | false |
JSONPatchOperation
JSONPAtch operation
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
op | JSONPatch operation: add, copy, move, remove, replace, test | string | false |
path | Execute the operation to the given path | string | false |
value | Optional value to be used in the operation | interface{} | false |
6.3 - Kubernetes to Bucket
6.3.1 - Introduction
Kubernetes objects can be synchronized into a Bucket the kubernetes-to-bucket plugin.
Synchronization process
Special rules
There are no special rules for this synchronization plugin.
Blacklisted objects
There are some Kubernetes objects that are blacklisted by default and will be ignored by the synchronization process.
This is the list of the blacklisted objects:
- Namespaces which name starts with
kube-oropenshift, an the Namespaceresiliency-operator. - All namespaced objects inside a blacklisted Namespace.
- ConfigMaps named
kube-root-ca.crtoropenshift-service-ca.crt.
Objects path
Each Kubernetes object will be stored into a file with the following path: <group>.<version>.<kind>/<object_namespace>.<object_name>.
Examples:
- The Namespace named
testwill be saved in the filecore.v1.Namespace/test. - The Deployment named
app-1deployed in thetestNamespace will be saved in the fileapps.v1.Deployment/test.app-1.
Use cases
Backups
Backup your Kubernetes cluster to a Bucket to recover data when required.
Pilot light architecture
Synchronize applications to a Bucket and recover the applications in another cluster after a disaster.
6.3.2 - Configuration
Introduction
The synchronization process can be configured with some specific parameters using the .spec.config attribute.
apiVersion: automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: Synchronization
metadata:
name: example
spec:
plugin: kubernetes-to-bucket
config:
...
Required configuration
Source and destination
The source cluster and the destination bucket can be specified using the .spec.config.sourceName and .spec.config.destinationName properties. Both the KubernetesCluster and the bucket objects should exists in the same Namespace where the synchronization is being created.
Example:
apiVersion: automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: Synchronization
metadata:
name: example
spec:
plugin: kubernetes-to-bucket
config:
sourceName: cluster-1
destinationName: bucket-1
...
Optional configuration
Selectors
The resources that should be synchronized can be configured using the .spec.config.selectors property. If not configured, all resources will be included in the synchronization.
Example:
apiVersion: automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: Synchronization
metadata:
name: example
spec:
plugin: kubernetes-to-bucket
config:
...
selectors:
- target:
version: v1
resources:
- namespaces
objectSelector:
labelSelector:
matchLabels:
disaster-recovery: "true"
Global selectors
Global selectors are used to set the default value on all selectors defined in .spec.config.selectors. They can be configured with the .spec.config.globalSelector property.
There are two options allowed, that can be configured at the same time:
namespaceSelector: to set e dafult namespace selector for namespaced resourcesobjectSelector: to set a default object selector for all resources
Example:
apiVersion: automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: Synchronization
metadata:
name: example
spec:
plugin: kubernetes-to-bucket
config:
...
globalSelector:
namespaceSelector:
labelSelector:
matchLabels:
env: pro
objectSelector:
labelSelector:
matchLabels:
env: pro
Path prefix
The Kubernetes objects can be written in a subdirectory of the destination Bucket. The property .spec.config.pathPrefix allows this configuration.
Example:
apiVersion: automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: Synchronization
metadata:
name: example
spec:
plugin: kubernetes-to-bucket
config:
...
pathPrefix: prefix-path
Log level
The log level of the Pod deployed to execute the synchronization, can be configured with the .spec.config.logLevel parameter.
info.
Accepted values: debug, info, warn, error.Example:
apiVersion: automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: Synchronization
metadata:
name: example
spec:
plugin: kubernetes-to-bucket
config:
...
logLevel: warn
Observability
Observability can be enaled using the specific .spec.config.observability parameter. For more information check the Observability page.
Default value:
enabled: false
interval: 60s
Example:
apiVersion: automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: Synchronization
metadata:
name: example
spec:
plugin: kubernetes-to-bucket
config:
...
observability:
enabled: true
interval: 2m
Limit assigned resources
For each synchronization, a new Pod is deployed inside the same Namespace. The limit and requests resources can be set using the .spec.config.resources field.
{}.Example:
apiVersion: automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: Synchronization
metadata:
name: example
spec:
plugin: kubernetes-to-bucket
config:
...
resources:
requests:
cpu: 1
memory: 2Gi
limits:
cpu: 2
memory: 2Gi
Concurrency
The concurrency parameter can be used to improve the peformance of the synchronization process with .spec.config.concurrency`.
100.Example:
apiVersion: automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: Synchronization
metadata:
name: example
spec:
plugin: kubernetes-to-bucket
config:
...
concurrency: 200
Transformations
Kubernetes obejcts from the source cluster can be transformed before being synchronized into the destination bucket.
Example:
apiVersion: automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: Synchronization
metadata:
name: example
spec:
plugin: kubernetes-to-bucket
config:
...
transformations:
resources:
- version: v1
resources:
- namespaces
operations:
- jsonpatch:
operations:
- op: add
path: /metadata/labels/test-astrosync
value: ok
6.3.3 - Observability
Introduction
The synchronization process exports many metrics in Prometheus format over HTTP.
Exported metrics
The following metrics are available:
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
astronetes_synchronization_status | The status of each synchronization object. |
astronetes_synchronization_status_total | The count of synchronization objects for each state. |
Requirements
- The
ServiceMonitorCRD from prometheus (servicemonitors.monitoring.coreos.com) must be enabled in the cluster where the operator is running.
Processes
Enable observability
Update the synchronization configuration, setting the paramente .spec.config.observability.enabled to true.
Once enabled the observability, a ServiceMonitor will be created in the same Namespace of the related synchronization.
Disable observability
Update the synchronization configuration, setting the paramente .spec.config.observability.enabled to false.
6.3.4 - API Reference
Config
Configuration for Kubernetes to Bucket synchronization
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
concurrency | Concurrent processes to be executed to improve performance | int | false |
destinationName | Bucket name where data will be synchronized | string | false |
globalSelector | Overrides selectors properties | KubernetesGlobalSelector | false |
logLevel | Log level to be used by the synchronization Pod | string | false |
observability | Observability configuration | ObservabilityConfig | false |
options | Synchronization options | SynchronizationOptions | false |
pathPrefix | Path prefix to be used to retreive objects in the Bucket | string | false |
resources | Resources to be assigned to the synchronization Pod | ResourceRequirements | false |
selectors | Selectors to filter the Kubernetes resources to be synchronized | []KubernetesObjectSelector | false |
sourceName | KubernetesCluster name from where data will be read | string | false |
transformations | Transform Kubernetes objects before to be written to the destination | []Transformations | false |
useCachedData | Use cached data instead of get data from assets on startup | bool | false |
KubernetesGlobalSelector
Global selector is used to set the default value on all selectors
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
objectSelector | Rules to filter Kubernetes objects by ObjectSelector | ObjectSelector | false |
namespaceSelector | Rules to filter Kubernetes objects by NamespaceSelector | NamespaceSelector | false |
ObjectSelector
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
nameSelector | Filter objects by their name | NameSelector | false |
labelSelector | Filter objects by their labels | LabelSelector | false |
NameSelector
Select object by their name
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
includeRegex | Include names that matches at least one regex | []string | false |
excludeRegex | Exlcude names that matches at least one regex | []string | false |
LabelSelector
A label selector is a label query over a set of resources. The result of matchLabels and matchExpressions are ANDed. An empty label selector matches all objects. A null label selector matches no objects. +structType=atomic
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
matchLabels | matchLabels is a map of {key,value} pairs. A single {key,value} in the matchLabelsmap is equivalent to an element of matchExpressions, whose key field is “key”, theoperator is “In”, and the values array contains only “value”. The requirements are ANDed.+optional | map[string]string | false |
matchExpressions | matchExpressions is a list of label selector requirements. The requirements are ANDed.+optional+listType=atomic | []LabelSelectorRequirement | false |
LabelSelectorRequirement
A label selector requirement is a selector that contains values, a key, and an operator that relates the key and values.
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
key | key is the label key that the selector applies to. | string | false |
operator | operator represents a key’s relationship to a set of values.Valid operators are In, NotIn, Exists and DoesNotExist. | LabelSelectorOperator | false |
values | values is an array of string values. If the operator is In or NotIn,the values array must be non-empty. If the operator is Exists or DoesNotExist,the values array must be empty. This array is replaced during a strategicmerge patch.+optional+listType=atomic | []string | false |
LabelSelectorOperator
A label selector operator is the set of operators that can be used in a selector requirement.
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|
NamespaceSelector
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
nameSelector | Filter Namespaces by their name | NameSelector | false |
labelSelector | Filter Namespaces by their labels | LabelSelector | false |
ObservabilityConfig
Configure the synchronization process observability using Prometheus ServiceMonitor
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
enabled | Enable the Observability with a Prometheus ServiceMonitor | bool | false |
interval | Configure the interval in the ServiceMonitor that Prometheus will use to scrape metrics | Duration | false |
Duration
Duration is a wrapper around time.Duration which supports correct marshaling to YAML and JSON. In particular, it marshals into strings, which can be used as map keys in json.
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|
SynchronizationOptions
Customize the synchronization process with special options
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
dryRun | Simulate the synchronization process but don’t execute the write operations | bool | false |
forceSync | Synchronize object in the destination even if the object exists in the destination and it doesn’t match the configured selectors | bool | false |
forcePrune | Prune object in the destination even if it doesn’t match the configured selectors | bool | false |
showLogIfObjectIsAlreadyInSync | Show a log message if object is already in sync | bool | false |
showLogIfObjectHaveBeenAdapted | Show a log message if object have been adapted for the destination | bool | false |
KubernetesObjectSelector
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
objectSelector | Filter objects by ObjectSelector | ObjectSelector | false |
namespaceSelector | Filter objects by NamespaceSelector | NamespaceSelector | false |
target | Kubernetes resource to be used | GroupVersionResources | false |
GroupVersionResources
Select a set of GroupVersionResource
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
group | Kubernetes resource group. Example: apps | string | false |
version | Kubernetes resource version. Example: v1 | string | false |
resources | Kubernetes resource names. Example: deployments | []string | false |
Transformations
Transformations is a list of operations to modifiy the Kubernetes objects matching the given selectors
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
resources | Select the objects to be transfomred by their resource type | []GroupVersionResources | false |
namespaceSelector | Filter the objects to be transformed by NamespaceSelector | NamespaceSelector | false |
objectSelector | Filter the objects to be transformed by ObjectSelector | ObjectSelector | false |
operations | Operations to be executed to transform the objects | []TransformationOperation | false |
TransformationOperation
The operation to execute to transform the objects
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
jsonpatch | JSONPatch operation | OperationJSONPatch | false |
OperationJSONPatch
The JSONPatch operation
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
skipIfNotFoundOnDelete | Skip if not found on delete | bool | false |
operations | List of operations to be executed | []JSONPatchOperation | false |
JSONPatchOperation
JSONPAtch operation
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
op | JSONPatch operation: add, copy, move, remove, replace, test | string | false |
path | Execute the operation to the given path | string | false |
value | Optional value to be used in the operation | interface{} | false |
6.4 - Kubernetes to Kubernetes
6.4.1 - Introduction
Kubernetes objects can be synchronized between clusters adopting the kubernetes-to-kubernetes plugin.
Synchronization process
Special rules
Additionally, there are some special rules for source kind of objects:
PersistentVolumeClaim: objects will be updated in the destination cluster only if
.spec.resourceschanges.ServiceAccount: If you’re using a Kubernetes cluster version <v1.24, when creating a ServiceAccount, an autogenerated secret will be created. From here, there are two scenarios:
Service account with an autogenerated secret: The autogenerated secret will be deleted, and a new one will be generated in the target cluster. The secret is always updated during each synchronization.
Service account with a custom secret: The custom secret will remain unchanged.
To avoid errors, custom secrets must not follow the autogenerated secret naming structure. Secrets are considered autogenerated if they begin with the following prefixes:
{serviceAccountName}-token-{serviceAccountName}-dockercfg-
Blacklisted objects
There are some Kubernetes objects that are blacklisted by default and will be ignored by the synchronization process.
This is the list of the blacklisted objects:
- Namespaces which name starts with
kube-oropenshift, and the Namespaceresiliency-operator. - All namespaced objects inside a blacklisted Namespace.
- ConfigMaps named
kube-root-ca.crtoropenshift-service-ca.crt.
6.4.2 - Configuration
Introduction
The synchronization process can be configured with some specific parameters using the .spec.config attribute.
apiVersion: automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: Synchronization
metadata:
name: example
spec:
plugin: kubernetes-to-kubernetes
config:
...
Required configuration
Source and destination
The source and the destination clusters can be specified using the .spec.config.sourceName and .spec.config.destinationName properties. Both KubernetesCluster objects should exists in the same Namespace where the synchronization is being created.
Example:
apiVersion: automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: Synchronization
metadata:
name: example
spec:
plugin: kubernetes-to-kubernetes
config:
sourceName: cluster-1
destinationName: cluster-2
...
Selectors
The resources that should be synchronized between clusters can be configured using the .spec.config.selectors property.
Example:
apiVersion: automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: Synchronization
metadata:
name: example
spec:
plugin: kubernetes-to-kubernetes
config:
...
selectors:
- target:
version: v1
resources:
- namespaces
objectSelector:
labelSelector:
matchLabels:
disaster-recovery: "true"
Optional configuration
Global selectors
Global selectors are used to set the default value on all selectors defined in .spec.config.selectors. They can be configured with the .spec.config.globalSelector property.
There are two options allowed, that can be configured at the same time:
namespaceSelector: to set e dafult namespace selector for namespaced resourcesobjectSelector: to set a default object selector for all resources
Example:
apiVersion: automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: Synchronization
metadata:
name: example
spec:
plugin: bucket-to-kubernetes
config:
...
globalSelector:
namespaceSelector:
labelSelector:
matchLabels:
env: pro
objectSelector:
labelSelector:
matchLabels:
env: pro
Log level
The log level of the Pod deployed to execute the synchronization, can be configured with the .spec.config.logLevel parameter.
info.
Accepted values: debug, info, warn, error.Example:
apiVersion: automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: Synchronization
metadata:
name: example
spec:
plugin: kubernetes-to-kubernetes
config:
...
logLevel: warn
Observability
Observability can be enaled using the specific .spec.config.observability parameter.
Default value:
enabled: false
interval: 60s
Example:
apiVersion: automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: Synchronization
metadata:
name: example
spec:
plugin: kubernetes-to-kubernetes
config:
...
observability:
enabled: true
interval: 2m
Limit assigned resources
For each synchronization, a new Pod is deployed inside the same Namespace. The limit and requests resources can be set using the .spec.config.resources field.
{}.Example:
apiVersion: automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: Synchronization
metadata:
name: example
spec:
plugin: kubernetes-to-kubernetes
config:
...
resources:
requests:
cpu: 1
memory: 2Gi
limits:
cpu: 2
memory: 2Gi
Concurrency
The concurrency parameter can be used to improve the peformance of the synchronization process with .spec.config.concurrency`.
100.Example:
apiVersion: automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: Synchronization
metadata:
name: example
spec:
plugin: kubernetes-to-kubernetes
config:
...
concurrency: 200
Transformations
Kubernetes obejcts from the source cluster can be transformed before being synchronized into the destination cluster.
Example:
apiVersion: automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: Synchronization
metadata:
name: example
spec:
plugin: kubernetes-to-kubernetes
config:
...
transformations:
- resources:
- group: ""
version: v1
resources:
- namespaces
namespaceSelector:
labelSelector:
matchLabels:
sync: "true"
operations:
- jsonpatch:
operations:
- op: add
path: /metadata/labels/test-astrosync
value: ok
6.4.3 - Observability
Introduction
The synchronization process exports many metrics in Prometheus format over HTTP.
Exported metrics
The following metrics are available:
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
astronetes_synchronization_status | The status of each synchronization object. |
astronetes_synchronization_status_total | The count of synchronization objects for each state. |
Requirements
- The
ServiceMonitorCRD from prometheus (servicemonitors.monitoring.coreos.com) must be enabled in the cluster where the operator is running.
Processes
Enable observability
Update the synchronization configuration, setting the paramente .spec.config.observability.enabled to true.
Once enabled the observability, a ServiceMonitor will be created in the same Namespace of the related synchronization.
Disable observability
Update the synchronization configuration, setting the paramente .spec.config.observability.enabled to false.
6.4.4 - API Reference
Config
Configuration for Kubernetes to Kubernetes synchronization
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
concurrency | Concurrent processes to be executed to improve performance | int | false |
destinationName | KubernetesCluster name where data will be synchronized | string | false |
globalSelector | Overrides selectors properties | KubernetesGlobalSelector | false |
logLevel | Log level to be used by the synchronization Pod | string | false |
observability | Observability configuration | ObservabilityConfig | false |
options | Synchronization options | SynchronizationOptions | false |
resources | Resources to be assigned to the synchronization Pod | ResourceRequirements | false |
selectors | Selectors to filter the Kubernetes resources to be synchronized | []KubernetesObjectSelector | false |
sourceName | KubernetesCluster name from where data will be read | string | false |
transformations | Transform Kubernetes objects before to be written to the destination | []Transformations | false |
useCachedData | Use cached data instead of get data from Kubernetes clusters on startup | bool | false |
KubernetesGlobalSelector
Global selector is used to set the default value on all selectors
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
objectSelector | Rules to filter Kubernetes objects by ObjectSelector | ObjectSelector | false |
namespaceSelector | Rules to filter Kubernetes objects by NamespaceSelector | NamespaceSelector | false |
ObjectSelector
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
nameSelector | Filter objects by their name | NameSelector | false |
labelSelector | Filter objects by their labels | LabelSelector | false |
NameSelector
Select object by their name
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
includeRegex | Include names that matches at least one regex | []string | false |
excludeRegex | Exlcude names that matches at least one regex | []string | false |
LabelSelector
Select object by their labels
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
matchLabels | Match object by the given labels | map[string]string | false |
matchExpressions | Match object by the given expressions | []LabelSelectorRequirement | false |
LabelSelectorRequirement
A label selector requirement is a selector that contains values, a key, and an operator that relates the key and values.
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
key | key is the label key that the selector applies to. | string | false |
operator | operator represents a key’s relationship to a set of values.Valid operators are In, NotIn, Exists and DoesNotExist. | LabelSelectorOperator | false |
values | values is an array of string values. If the operator is In or NotIn,the values array must be non-empty. If the operator is Exists or DoesNotExist,the values array must be empty. This array is replaced during a strategicmerge patch.+optional+listType=atomic | []string | false |
LabelSelectorOperator
A label selector operator is the set of operators that can be used in a selector requirement.
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|
NamespaceSelector
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
nameSelector | Filter Namespaces by their name | NameSelector | false |
labelSelector | Filter Namespaces by their labels | LabelSelector | false |
ObservabilityConfig
Configure the synchronization process observability using Prometheus ServiceMonitor
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
enabled | Enable the Observability with a Prometheus ServiceMonitor | bool | false |
interval | Configure the interval in the ServiceMonitor that Prometheus will use to scrape metrics | Duration | false |
Duration
Duration is a wrapper around time.Duration which supports correct marshaling to YAML and JSON. In particular, it marshals into strings, which can be used as map keys in json.
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|
SynchronizationOptions
Customize the synchronization process with special options
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
dryRun | Simulate the synchronization process but don’t execute the write operations | bool | false |
forceSync | Synchronize object in the destination even if the object exists in the destination and it doesn’t match the configured selectors | bool | false |
forcePrune | Prune object in the destination even if it doesn’t match the configured selectors | bool | false |
showLogIfObjectIsAlreadyInSync | Show a log message if object is already in sync | bool | false |
showLogIfObjectHaveBeenAdapted | Show a log message if object have been adapted for the destination | bool | false |
KubernetesObjectSelector
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
objectSelector | Filter objects by ObjectSelector | ObjectSelector | false |
namespaceSelector | Filter objects by NamespaceSelector | NamespaceSelector | false |
target | Kubernetes resource to be used | GroupVersionResources | false |
GroupVersionResources
Select a set of GroupVersionResource
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
group | Kubernetes resource group. Example: apps | string | false |
version | Kubernetes resource version. Example: v1 | string | false |
resources | Kubernetes resource names. Example: deployments | []string | false |
Transformations
Transformations is a list of operations to modifiy the Kubernetes objects matching the given selectors
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
resources | Select the objects to be transfomred by their resource type | []GroupVersionResources | false |
namespaceSelector | Filter the objects to be transformed by NamespaceSelector | NamespaceSelector | false |
objectSelector | Filter the objects to be transformed by ObjectSelector | ObjectSelector | false |
operations | Operations to be executed to transform the objects | []TransformationOperation | false |
TransformationOperation
The operation to execute to transform the objects
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
jsonpatch | JSONPatch operation | OperationJSONPatch | false |
OperationJSONPatch
The JSONPatch operation
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
skipIfNotFoundOnDelete | Skip if not found on delete | bool | false |
operations | List of operations to be executed | []JSONPatchOperation | false |
JSONPatchOperation
JSONPAtch operation
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
op | JSONPatch operation: add, copy, move, remove, replace, test | string | false |
path | Execute the operation to the given path | string | false |
value | Optional value to be used in the operation | interface{} | false |
6.5 - Zookeeper to Zookeeper
6.5.1 - Introduction
You can synchronize Zookeeper data between two clusters using the Zookeeper protocol.
Supported models
One time synchronization
You can synchronize the data just once with the Synchronization Kubernetes object.
Periodic synchronization
You can synchronize periodically the SynchronizationPlan Kubernetes object.
Samples
Synchronize once
Synchronize the data once only in the /test path:
apiVersion: automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: Synchronization
metadata:
generateName: synchronize-zookeeper-
spec:
plugin: zookeeper-to-zookeeper-nodes
config:
sourceName: zookeeper-source
destinationName: zookeeper-destination
rootPath: /test
createRoutePath: true
Scheduled synchronization
Synchronize data every hour in the /test path:
apiVersion: automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: SynchronizationPlan
metadata:
name: synchronize-zookeeper
spec:
schedule: "0 * * * *"
template:
spec:
plugin: zookeeper-to-zookeeper-nodes
config:
sourceName: zookeeper-source
destinationName: zookeeper-destination
rootPath: /test
6.5.2 - Configuration
Required configuration
Source and destination
The source and the destination clusters can be specified using the .spec.config.sourceName and .spec.config.destinationName properties. Both Database objects should exists in the same Namespace where the synchronization is being created.
Example:
apiVersion: automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: Synchronization
metadata:
name: example
spec:
plugin: zookeeper-nodes-to-zookeeper
config:
sourceName: cluster-1
destinationName: cluster-2
...
Root path
The root path to be used to only synchronize a specific part of the Zookeeper database.
Example:
apiVersion: automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: Synchronization
metadata:
name: example
spec:
plugin: zookeeper-nodes-to-zookeeper
config:
...
rootPath: /test
Optional configuration
Create root path
Create the Root Path in the destination database if it doesn’t exist.
falseExample:
apiVersion: automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: Synchronization
metadata:
name: example
spec:
plugin: zookeeper-nodes-to-zookeeper
config:
...
createRootPath: true
Ignore ephemeral
Don’t synchronize ephemeral data in the destination cluster..
falseExample:
apiVersion: automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: Synchronization
metadata:
name: example
spec:
plugin: zookeeper-nodes-to-zookeeper
config:
...
ignoreEphemeral: true
Exclude paths
Exclude data from being synchronized to the destination cluster filtering on path using regex.
Example:
apiVersion: automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: Synchronization
metadata:
name: example
spec:
plugin: zookeeper-nodes-to-zookeeper
config:
...
excludeRegex: ..
6.5.3 - API Reference
Config
Configuration for Zookeeper to Zookeeper synchronization
| Name | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
sourceName | Zookeeper instance acting as source | string | yes |
destinationName | Zookeeper instance acting as destination | string | yes |
rootPath | Root Path of the contents to synchronize | string | yes |
createRootPath | Whether to create the Root Path in the destination database | boolean | no |
ignoreEphemeral | Whether to ignore ephemeral | boolean | no |
excludePathRegexp | Regular expression for keys to exclude while synchronizing | string | no |
7 - Automation
7.1 - Introduction
The operations to improve the platform resiliency can be automated with the automation framework provided by the Resiliency Operator.
Use cases
Recovery from a disaster
After a disaster occurs in one of your platform assets, the automation framework help in the recovery of the platform.
Key concepts
Tasks
A Task represents a configurable, reusable unit of work. It defines a plugin with a specific configuration to be executed later.
TaskRuns
A TaskRun represents a single execution of a Task. When a TaskRun is created, it triggers the execution of the plugin defined in the Task.
7.2 - Plugins
7.2.1 - Custom image
7.2.1.1 - Introduction
The custom-image plugins enables the deployment of a custom image to be executed as Task. This is extremely useful to run custom logic and software in the resiliency patterns.
The Pod is deployed in the Kubernetes namespace where the Task has been created.
7.2.1.2 - Configuration
Task
Configuration
| Name | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| image | Container image to be deployed | string | yes |
| command | The command to be executed when the container starts | []string | yes |
7.2.1.3 - Samples
This is a list of samples of what can be perfomed as Task with the custom-image plugin.
Bash command
Run a bash command:
apiVersion: automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: Task
metadata:
name: hello-world
spec:
plugin: custom-image
config:
image: busybox
command:
- echo
- "hello world"
Kubectl command
Execute a kubectl command:
apiVersion: automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: Task
metadata:
name: kubectl
spec:
plugin: custom-image
config:
image: bitnami/kubectl:1.27
command:
- kubectl
- cluster-info
clusterRole: cluster-admin
7.2.2 - Kubernetes object transformation
7.2.2.1 - Introduction
The custom-image plugins enables the deployment of a custom image to be executed as Task. This is extremely useful to run custom logic and software in the resiliency patterns.
7.2.2.2 - Configuration
Task
Configuration
| Name | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| image | Container image to be deployed | string | yes |
| command | The command to be executed when the container starts | []string | yes |
7.2.3 - Run synchronization
7.2.3.1 - Introduction
This plugins allows the creation of new Synchronization objects on demands, using a custom template.
Use cases
Disaster Recovery
Create a Synchronization process to restore data after a disaster occurs
Computing offloading
Explaind the platform offloading the applications in another cloud provider.
7.2.3.2 - Configuration
Introduction
The Task can be configured with some specific parameters using the .spec.config attribute.
Required
Plugin
The .spec.plugin reference to the plugin to be used by the Task. This value must be set to run-synchronization.
Example:
apiVersion: automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: Task
metadata:
name: example
spec:
plugin: run-synchronization
...
Synchronization spec
Configure the synchronization spec according to the plugin to be used by the synchronization.
Example:
apiVersion: automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: Task
metadata:
name: set-replica-to-1
spec:
plugin: run-synchronization
config:
template:
spec:
plugin: kubernetes-to-kubernetes
config:
sourceName: ...
destinationName: ...
...
Optional
Synchronization annotations
The annotations for the Synchronization object can be configured using the .spec.config.template.metadata.annotations field.
Example:
apiVersion: automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: Task
metadata:
name: set-replica-to-1
spec:
plugin: run-synchronization
config:
template:
metadata:
annotations:
env: dev
spec:
plugin: kuberentes-to-kubernetes
config:
sourceName: ...
destinationName: ...
...
Synchronization labels
The labels for the Synchronization object can be configured using the .spec.config.template.metadata.labels field.
Example:
apiVersion: automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: Task
metadata:
name: set-replica-to-1
spec:
plugin: run-synchronization
config:
template:
metadata:
labels:
env: dev
spec:
plugin: kuberentes-to-kubernetes
config:
sourceName: ...
destinationName: ...
...
7.2.3.3 - API Reference
Config
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
template | Template | false |
Template
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
spec | SynchronizationSpec | false |
SynchronizationSpec
SynchronizationSpec defines the desired state of Synchronization
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
restartPolicy | Restart policy | RestartPolicy | false |
plugin | Synchronization plugin | SynchronizationPlugin | false |
config | Synchronization config | JSON | false |
SynchronizationPlugin
| Field | Description | Type | Required |
|---|
8 - Tutorials
8.1 - Active-active Kubernetes architecture
Overview
Active-active replication between Kubernetes clusters is a strategy to ensure high availability and disaster recovery for applications. In this setup, multiple Kubernetes clusters, typically located in different geographical regions, run identical copies of an application simultaneously.
Prerequisites
- Install Astronetes Resiliency Operator.
- Create a namespace where to store the secrets and run the synchronization between clusters.
Setup
Import the first cluster
Import the first Kubernetes cluster as described in details here:
Save the kubeconfig file as
cluster-1-kubeconfig.yaml.Import the kubeconfig file as secret:
kubectl create secret generic cluster-1-kubeconfig --from-file=kubeconfig.yaml=cluster-1-kubeconfig.yamlCreate the KubernetesCluster resource manifest
cluster-1.yaml:apiVersion: assets.astronetes.io/v1alpha1 kind: KubernetesCluster metadata: name: cluster-1 spec: secretName: cluster-1-kubeconfigDeploy the resource with the following command:
kubectl create -f cluster-1.yaml
Import the second cluster
Import the first Kubernetes cluster as described in details here:
Save the kubeconfig file as
cluster-2-kubeconfig.yaml.Import the kubeconfig file as secret:
kubectl create secret generic cluster-2-kubeconfig --from-file=kubeconfig.yaml=cluster-2-kubeconfig.yamlCreate the KubernetesCluster resource manifest
cluster-2.yaml:apiVersion: assets.astronetes.io/v1alpha1 kind: KubernetesCluster metadata: name: cluster-2 spec: secretName: cluster-2-kubeconfigDeploy the resource with the following command:
kubectl create -f cluster-2.yaml
Synchronize the clusters
Create the configuration manifest to synchronize the clusters according to the full documentation is provided at Configure kubernetes-to-kubernetes.
In the following examples there is a minimal configuration to synchronize namespaces labeled with sync=true:
- Save the configuration file as
livesync.yamlwith the following content:
apiVersion: automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: LiveSynchronization
metadata:
name: livesync-dev-active-active
spec:
plugin: kubernetes-to-kubernetes
config:
sourceName: cluster-1
destinationName: cluster-2
globalSelector:
namespaceSelector:
labelSelector:
matchLabels:
sync: true
observability:
enabled: true
options:
dryRun: false
selectors:
- objectSelector:
labelSelector:
matchLabels:
sync: true
target:
group: ""
resources:
- namespaces
version: v1
- target:
group: ""
resources:
- services
- secrets
- configmaps
- serviceaccounts
version: v1
- target:
group: apps
resources:
- deployments
version: v1
- target:
group: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
resources:
- clusterroles
- rolebindings
version: v1
- target:
group: networking.k8s.io
resources:
- ingresses
version: v1
suspend: false
Apply the configuration:
kubectl apply -f livesync.yaml
Operations
Pause the synchronization
The synchronization process can be paused with the following command:
kubectl patch livesynchronization active-active -p '{"spec":{"suspend":true}}' --type=merge
Resume the synchronization
The synchronization process can be paused with the following command:
kubectl patch livesynchronization active-active -p '{"spec":{"suspend":false}}' --type=merge
8.2 - Active-passive Kubernetes architecture
Overview
Active-passive replication between Kubernetes clusters is a strategy designed to provide high availability and disaster recovery, albeit in a more cost-efficient manner than active-active replication.
Prerequisites
- Install Astronetes Resiliency Operator.
- Create a namespace where to store the secrets and run the synchronization between clusters.
Setup
Import the active cluster
Import the first Kubernetes cluster as described in details here:
Save the kubeconfig file as
cluster-1-kubeconfig.yaml.Import the kubeconfig file as secret:
kubectl create secret generic cluster-1-kubeconfig --from-file=kubeconfig.yaml=cluster-1-kubeconfig.yamlCreate the KubernetesCluster resource manifest
cluster-1.yaml:apiVersion: assets.astronetes.io/v1alpha1 kind: KubernetesCluster metadata: name: cluster-1 spec: secretName: cluster-1-kubeconfigDeploy the resource with the following command:
kubectl create -f cluster-1.yaml
Import the passive cluster
Import the first Kubernetes cluster as described in details here:
Save the kubeconfig file as
cluster-2-kubeconfig.yaml.Import the kubeconfig file as secret:
kubectl create secret generic cluster-2-kubeconfig --from-file=kubeconfig.yaml=cluster-2-kubeconfig.yamlCreate the KubernetesCluster resource manifest
cluster-2.yaml:apiVersion: assets.astronetes.io/v1alpha1 kind: KubernetesCluster metadata: name: cluster-2 spec: secretName: cluster-2-kubeconfigDeploy the resource with the following command:
kubectl create -f cluster-2.yaml
Synchronize the clusters
Create the configuration manifest to synchronize the clusters according to the full documentation is provided at Configure kubernetes-to-kubernetes.
In the following examples there is a minimal configuration to synchronize namespaces labeled with sync=true. The deployments are replicated to the second cluster with replica=0, meaning that the applicatio is deployed but not running in the cluster. Only after the switch to the second cluster, the application will be started.
- Save the configuration file as
livesync.yamlwith the following content:
apiVersion: automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: LiveSynchronization
metadata:
name: active-passive
spec:
plugin: kubernetes-to-kubernetes
config:
sourceName: cluster-1
destinationName: cluster-2
globalSelector:
namespaceSelector:
labelSelector:
matchLabels:
sync: "true"
observability:
enabled: true
options:
dryRun: false
transformations:
- resources:
- group: apps
version: v1
resources:
- deployments
namespaceSelector:
labelSelector:
matchLabels:
sync: "true"
operations:
- jsonpatch:
operations:
- op: replace
path: /spec/replicas
value: 0
selectors:
- objectSelector:
labelSelector:
matchLabels:
sync: "true"
target:
group: ""
resources:
- namespaces
version: v1
- target:
group: ""
resources:
- services
- secrets
- configmaps
- serviceaccounts
version: v1
- target:
group: apps
resources:
- deployments
version: v1
- target:
group: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
resources:
- clusterroles
- rolebindings
version: v1
- target:
group: networking.k8s.io
resources:
- ingresses
version: v1
suspend: false
Apply the configuration:
kubectl apply -f livesync.yaml
Operations
Pause the synchronization
The synchronization process can be paused with the following command:
kubectl patch livesynchronization active-passive -p '{"spec":{"suspend":true}}' --type=merge
Resume the synchronization
The synchronization process can be resumed with the following command:
kubectl patch livesynchronization active-passive -p '{"spec":{"suspend":false}}' --type=merge
Recover from disasters
Recovering from a disaster will require the deployment of a TaskRun resource per Task that applies to recover the system and applications.
Define the TaskRun resource in the
taskrun.yamlfile:apiVersion: automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1 kind: TaskRun metadata: name: restore-apps spec: taskName: set-test-labelCreate the TaskRun:
kubectl create -f taskrun.yamlWait for the application to be recovered.
Understanding the TaskRun
After defining a LiveSynchronization, a Task resource will be created in the destination cluster. The operator processes the spec.config.reaplication.resources[*].recoveryProcess parameter to define the required steps to activate the dormant applications.
This is the Task that will be created according to the previous defined LiveSynchronization object:
apiVersion: automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: Task
metadata:
name: active-passive
spec:
plugin: kubernetes-objects-transformation
config:
resources:
- identifier:
group: apps
version: v1
resources: deployments
patch:
operations:
- op: replace
path: '/spec/replicas'
value: 1
filter:
namespaceSelector:
matchLabels:
sync: "true"
For every Deployment in the selected namespaces, the pod replica will be set to 1.
This object should not be tempered with. It is managed by their adjacent LiveSynchronization.
8.3 - Synchronize Zookeeper clusters
Overview
In environments where high availability and disaster recovery are paramount, it is essential to maintain synchronized data across different ZooKeeper clusters to prevent inconsistencies and ensure seamless failover.
In the following tutorial will be explained how to synchronize Zookeeper clusters.
Prerequisites
- Install Astronetes Resiliency Operator.
- Create a namespace where to store the secrets and run the synchronization between clusters.
Setup
Import the first cluster
Import the first Zookeeper cluster as described in details here:
Define the Database resource with the following YAML, and save it as
zookeeper-1.yaml:apiVersion: assets.astronetes.io/v1alpha1 kind: Database metadata: name: zookeeper-1 spec: zookeeper: client: servers: - <zookeeper_ip>:<zookeeper_port> - <zookeeper_ip>:<zookeeper_port> - <zookeeper_ip>:<zookeeper_port>Import the resource with the following command:
kubectl create -f zookeeper-1.yaml
Import the second cluster
Import the second Zookeeper cluster as described in details here:
Define the Database resource with the following YAML, and save it as
zookeeper-2.yaml:apiVersion: assets.astronetes.io/v1alpha1 kind: Database metadata: name: zookeeper-2 spec: zookeeper: client: servers: - <zookeeper_ip>:<zookeeper_port> - <zookeeper_ip>:<zookeeper_port> - <zookeeper_ip>:<zookeeper_port>Import the resource with the following command:
kubectl create -f zookeeper-2.yaml
Synchronize the clusters
Create the configuration manifest to synchronize the clusters according to the full documentation is provided here:
In the following example there is the configuration to synchronize every hour all the data in the / path:
Create the synchronization file as
zookeeper-sync.yamlwith the following content:apiVersion: automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1 kind: SynchronizationPlan metadata: name: synchronize-zookeeper spec: schedule: "0 * * * *" template: spec: plugin: zookeeper-to-zookeeper-nodes config: sourceName: zookeeper-1 destinationName: zookeeper-2 rootPath: / createRoutePath: trueCustom path
The data to be synchronized between clusters can be specified inspec.template.spec.config.rootPath.Apply the configuration:
kubectl apply -f zookeeper-sync.yaml
Operations
Force the synchronization
The synchronization can be run at any time creating a Synchronization object.
In the following example there is the configuration to synchronize all the data in the / path:
- Create the synchronization file as
zookeeper-sync-once.yamlwith the following content:
apiVersion: automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: Synchronization
metadata:
generateName: synchronize-zookeeper-
spec:
plugin: zookeeper-to-zookeeper-nodes
config:
sourceName: zookeeper-1
destinationName: zookeeper-2
rootPath: /
createRoutePath: true
Apply the configuration:
kubectl create -f zookeeper-sync-once.yaml
9 - API Reference
This section contains the API Reference of CRDs for the Resiliency Operator.
9.1 - Assets API Reference
Packages
assets.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
Package v1alpha1 contains API Schema definitions for the assets v1alpha1 API group
Resource Types
AWSS3
Appears in:
| Field | Description | Default | Validation |
|---|---|---|---|
name string | Bucket name | Required: {} | |
region string | AWS region name | Required: {} | |
secretName string | Secret name where credentials are stored | Required: {} |
Bucket
Bucket is the Schema for the buckets API
Appears in:
| Field | Description | Default | Validation |
|---|---|---|---|
apiVersion string | assets.astronetes.io/v1alpha1 | ||
kind string | Bucket | ||
metadata ObjectMeta | Refer to Kubernetes API documentation for fields of metadata. | ||
spec BucketSpec |
BucketList
BucketList contains a list of Bucket
| Field | Description | Default | Validation |
|---|---|---|---|
apiVersion string | assets.astronetes.io/v1alpha1 | ||
kind string | BucketList | ||
metadata ListMeta | Refer to Kubernetes API documentation for fields of metadata. | ||
items Bucket array |
BucketSpec
BucketSpec defines the desired state of Bucket
Appears in:
| Field | Description | Default | Validation |
|---|---|---|---|
generic GenericBucket | Reference a generic bucket | Optional: {} | |
gcpCloudStorage GCPCloudStorage | Reference a GCP Cloud Storage service | Optional: {} | |
awsS3 AWSS3 | Reference a AWS Bucket service | Optional: {} |
Database
Database is the Schema for the databases API
Appears in:
| Field | Description | Default | Validation |
|---|---|---|---|
apiVersion string | assets.astronetes.io/v1alpha1 | ||
kind string | Database | ||
metadata ObjectMeta | Refer to Kubernetes API documentation for fields of metadata. | ||
spec DatabaseSpec |
DatabaseList
DatabaseList contains a list of Database
| Field | Description | Default | Validation |
|---|---|---|---|
apiVersion string | assets.astronetes.io/v1alpha1 | ||
kind string | DatabaseList | ||
metadata ListMeta | Refer to Kubernetes API documentation for fields of metadata. | ||
items Database array |
DatabaseSpec
DatabaseSpec defines the desired state of Database
Appears in:
| Field | Description | Default | Validation |
|---|---|---|---|
zookeeper Zookeeper | Zookeeper database | Optional: {} |
GCPCloudStorage
Appears in:
| Field | Description | Default | Validation |
|---|---|---|---|
name string | Bucket name | Required: {} | |
secretName string | Secret name where credentials are stored | Required: {} |
GenericBucket
Appears in:
| Field | Description | Default | Validation |
|---|---|---|---|
name string | Bucket name | Required: {} | |
endpoint string | Bucket endpoint | Required: {} | |
useSSL boolean | Use SSL | Optional: {} | |
secretName string | Secret name where credentials are stored | Required: {} |
KubernetesCluster
KubernetesCluster is the Schema for the kubernetesclusters API
Appears in:
| Field | Description | Default | Validation |
|---|---|---|---|
apiVersion string | assets.astronetes.io/v1alpha1 | ||
kind string | KubernetesCluster | ||
metadata ObjectMeta | Refer to Kubernetes API documentation for fields of metadata. | ||
spec KubernetesClusterSpec |
KubernetesClusterList
KubernetesClusterList contains a list of KubernetesCluster
| Field | Description | Default | Validation |
|---|---|---|---|
apiVersion string | assets.astronetes.io/v1alpha1 | ||
kind string | KubernetesClusterList | ||
metadata ListMeta | Refer to Kubernetes API documentation for fields of metadata. | ||
items KubernetesCluster array |
KubernetesClusterSpec
KubernetesClusterSpec defines the desired state of KubernetesCluster
Appears in:
| Field | Description | Default | Validation |
|---|---|---|---|
secretName string | Reference to the secret that stores the cluster Kubeconfig | Required: {} |
Zookeeper
Appears in:
| Field | Description | Default | Validation |
|---|---|---|---|
admin ZookeeperAdmin | Credentials for the admin port | Optional: {} | |
client ZookeeperClient | Credentials for the client port | Optional: {} |
ZookeeperAdmin
Appears in:
| Field | Description | Default | Validation |
|---|---|---|---|
protocol string | Zookeeper protocol | Required: {} | |
host string | Zookeeper host | Required: {} | |
port string | Zookeeper port | Required: {} | |
secretName string | Zookeeper authentication data | Optional: {} |
ZookeeperClient
Appears in:
| Field | Description | Default | Validation |
|---|---|---|---|
servers string array | Zookeeper servers | Required: {} |
9.2 - Automation API Reference
Packages
automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
Package v1alpha1 contains API Schema definitions for the automation v1alpha1 API group
Resource Types
- Backup
- BackupList
- LiveSynchronization
- LiveSynchronizationList
- Synchronization
- SynchronizationList
- SynchronizationPlan
- SynchronizationPlanList
- Task
- TaskList
- TaskRun
- TaskRunList
Backup
Backup is the Schema for the backups API
Appears in:
| Field | Description | Default | Validation |
|---|---|---|---|
apiVersion string | automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1 | ||
kind string | Backup | ||
metadata ObjectMeta | Refer to Kubernetes API documentation for fields of metadata. | ||
spec BackupSpec |
BackupDestinationBucket
Appears in:
| Field | Description | Default | Validation |
|---|---|---|---|
name string | Reference the Bucket name | Required: {} | |
basePath string | The base path to be used to store the Backup data | Optional: {} |
BackupList
BackupList contains a list of Backup
| Field | Description | Default | Validation |
|---|---|---|---|
apiVersion string | automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1 | ||
kind string | BackupList | ||
metadata ListMeta | Refer to Kubernetes API documentation for fields of metadata. | ||
items Backup array |
BackupPlugin
Underlying type: string
Appears in:
BackupSourceDatabase
Appears in:
| Field | Description | Default | Validation |
|---|---|---|---|
name string | Reference the Database name | Required: {} |
BackupSourceKubernetesCluster
Appears in:
| Field | Description | Default | Validation |
|---|---|---|---|
name string | Reference the KubernetesCluster name | Required: {} | |
namespaces string array | Reference the Kubernetes namespaces to be included | Optional: {} |
BackupSpec
BackupSpec defines the desired state of Backup
Appears in:
| Field | Description | Default | Validation |
|---|---|---|---|
restartPolicy RestartPolicy | Suspend the CronJob | Optional: {} | |
plugin BackupPlugin | Backup plugin | Required: {} | |
config JSON | Synchronization config | Required: {} |
LiveSynchronization
LiveSynchronization is the Schema for the livesynchronizations API
Appears in:
| Field | Description | Default | Validation |
|---|---|---|---|
apiVersion string | automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1 | ||
kind string | LiveSynchronization | ||
metadata ObjectMeta | Refer to Kubernetes API documentation for fields of metadata. | ||
spec LiveSynchronizationSpec |
LiveSynchronizationList
LiveSynchronizationList contains a list of LiveSynchronization
| Field | Description | Default | Validation |
|---|---|---|---|
apiVersion string | automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1 | ||
kind string | LiveSynchronizationList | ||
metadata ListMeta | Refer to Kubernetes API documentation for fields of metadata. | ||
items LiveSynchronization array |
LiveSynchronizationPlugin
Underlying type: string
Appears in:
LiveSynchronizationSpec
LiveSynchronizationSpec defines the desired state of LiveSynchronization
Appears in:
| Field | Description | Default | Validation |
|---|---|---|---|
suspend boolean | Suspend the execution | false | Optional: {} |
plugin LiveSynchronizationPlugin | LiveSynchronization plugin | Required: {} | |
config JSON | LiveSynchronization config | Required: {} |
Resource
Appears in:
| Field | Description | Default | Validation |
|---|---|---|---|
group string | Resource group | Optional: {} | |
version string | Resource version | Required: {} | |
resource string | Resource | Required: {} |
Synchronization
Synchronization is the Schema for the synchronizations API
Appears in:
| Field | Description | Default | Validation |
|---|---|---|---|
apiVersion string | automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1 | ||
kind string | Synchronization | ||
metadata ObjectMeta | Refer to Kubernetes API documentation for fields of metadata. | ||
spec SynchronizationSpec |
SynchronizationList
SynchronizationList contains a list of Synchronization
| Field | Description | Default | Validation |
|---|---|---|---|
apiVersion string | automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1 | ||
kind string | SynchronizationList | ||
metadata ListMeta | Refer to Kubernetes API documentation for fields of metadata. | ||
items Synchronization array |
SynchronizationPlan
SynchronizationPlan is the Schema for the synchronizationplans API
Appears in:
| Field | Description | Default | Validation |
|---|---|---|---|
apiVersion string | automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1 | ||
kind string | SynchronizationPlan | ||
metadata ObjectMeta | Refer to Kubernetes API documentation for fields of metadata. | ||
spec SynchronizationPlanSpec |
SynchronizationPlanList
SynchronizationPlanList contains a list of SynchronizationPlan
| Field | Description | Default | Validation |
|---|---|---|---|
apiVersion string | automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1 | ||
kind string | SynchronizationPlanList | ||
metadata ListMeta | Refer to Kubernetes API documentation for fields of metadata. | ||
items SynchronizationPlan array |
SynchronizationPlanSpec
SynchronizationPlanSpec defines the desired state of SynchronizationPlan
Appears in:
| Field | Description | Default | Validation |
|---|---|---|---|
schedule string | Schedule in Cron format | Required: {} | |
startingDeadlineSeconds integer | Optional deadline in seconds for starting the job if it misses scheduled time for any reason. Missed jobs executions will be counted as failed ones. | Optional: {} | |
concurrencyPolicy ConcurrencyPolicy | Specifies how to treat concurrent executions of a Job. Valid values are: - “Allow” (default): allows CronJobs to run concurrently; - “Forbid”: forbids concurrent runs, skipping next run if previous run hasn’t finished yet; - “Replace”: cancels currently running job and replaces it with a new one | Optional: {} | |
suspend boolean | Suspend the execution | false | Optional: {} |
template SynchronizationTemplateSpec | Specify the Synchronization that will be created when executing the Cron | Optional: {} | |
successfulJobsHistoryLimit integer | The number of successful finished jobs to retain. Value must be non-negative integer | 2 | Optional: {} |
failedJobsHistoryLimit integer | The number of failed finished jobs to retain. Value must be non-negative integer | 2 | Optional: {} |
SynchronizationPlugin
Underlying type: string
Appears in:
SynchronizationSpec
SynchronizationSpec defines the desired state of Synchronization
Appears in:
| Field | Description | Default | Validation |
|---|---|---|---|
restartPolicy RestartPolicy | Restart policy | Optional: {} | |
plugin SynchronizationPlugin | Synchronization plugin | Required: {} | |
config JSON | Synchronization config | Required: {} |
SynchronizationTemplateSpec
Appears in:
| Field | Description | Default | Validation |
|---|---|---|---|
metadata ObjectMeta | Refer to Kubernetes API documentation for fields of metadata. | ||
spec SynchronizationSpec | Specification of the desired behavior of the Synchronization | Optional: {} |
Task
Task is the Schema for the tasks API
Appears in:
| Field | Description | Default | Validation |
|---|---|---|---|
apiVersion string | automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1 | ||
kind string | Task | ||
metadata ObjectMeta | Refer to Kubernetes API documentation for fields of metadata. | ||
spec TaskSpec |
TaskList
TaskList contains a list of Task
| Field | Description | Default | Validation |
|---|---|---|---|
apiVersion string | automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1 | ||
kind string | TaskList | ||
metadata ListMeta | Refer to Kubernetes API documentation for fields of metadata. | ||
items Task array |
TaskPlugin
Underlying type: string
Appears in:
TaskRun
TaskRun is the Schema for the taskruns API
Appears in:
| Field | Description | Default | Validation |
|---|---|---|---|
apiVersion string | automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1 | ||
kind string | TaskRun | ||
metadata ObjectMeta | Refer to Kubernetes API documentation for fields of metadata. | ||
spec TaskRunSpec |
TaskRunList
TaskRunList contains a list of TaskRun
| Field | Description | Default | Validation |
|---|---|---|---|
apiVersion string | automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1 | ||
kind string | TaskRunList | ||
metadata ListMeta | Refer to Kubernetes API documentation for fields of metadata. | ||
items TaskRun array |
TaskRunSpec
TaskRunSpec defines the desired state of TaskRun
Appears in:
| Field | Description | Default | Validation |
|---|---|---|---|
taskName string | Task name | Required: {} |
TaskSpec
TaskSpec defines the desired state of Task
Appears in:
| Field | Description | Default | Validation |
|---|---|---|---|
restartPolicy RestartPolicy | Restart policy | Optional: {} | |
plugin TaskPlugin | Task plugin | Required: {} | |
config JSON | Task config | Required: {} |