This is the multi-page printable view of this section. Click here to print.
Observability
1 - Audit fields
Auditing and version control is an important step when configuring resources. Knowing when a change was made and the account that applied it can be determinative in an ongoing investigation to solve an issue or a configuration mismanagement.
Audit fields
The following annotation are attached to every resource that belongs to Resiliency Operator Custom Resources:
apiVersion: automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: LiveSynchronization
metadata:
annotations:
audit.astronetes.io/last-update-time: "<date>" # Time at which the last update was applied.
audit.astronetes.io/last-update-user-uid: "<uid-hash>" # Hash representing the Unique Identifier of the user that applied the change.
audit.astronetes.io/last-update-username: "<username>" # Human readable name of the user that applied the change.
Example:
apiVersion: automation.astronetes.io/v1alpha1
kind: LiveSynchronization
metadata:
annotations:
audit.astronetes.io/last-update-time: "2024-02-09T14:05:30.67520525Z"
audit.astronetes.io/last-update-user-uid: "b3fd2a87-0547-4ff7-a49f-cce903cc2b61"
audit.astronetes.io/last-update-username: system:serviceaccount:preproduction:microservice1
Fields are updated only when a change to the fields .spec, .labels or .annotations are detected. Status modifications by the operator are not recorded.
Objects that are synchronized will not have these labels.
2 - Understanding logging
Disaster Recovery Operator implements a logging system throughout all its pieces so that the end user can have visibility on the system.
JSON fields
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| level | Log level at write time. |
| timestamp | Time at which the log was written. |
| msg | Log message. |
| process | Information about the process identity that generated the log. |
| event | Indicates if the log is referring to a create, update or delete action. |
| sourceObject | Object related to the source cluster that is being synchronized. |
| oldSourceObject | Previous state of the sourceObject. Only applicable to update events. |
| sourceCluster | Information about the source managed cluster. |
| destinationObject | Object related to the destination cluster. |
| destinationObject | Information about the destination managed cluster. |
| bucket | Recovery bucket information. |
| bucketObject | Path to the object to synchronize. |
| lastUpdate | Auditing information. More information. |
Examples
An object read from the source cluster.
{
"level": "info",
"timestamp": "2023-11-28T18:05:26.904276629Z",
"msg": "object read from cluster",
"process": {
"id": "eventslistener"
},
"sourceCluster": {
"name": "source",
"namespace": "dr-config",
"resourceVersion": "91015",
"uid": "3c39aaf0-4216-43a8-b23c-63f082b22436"
},
"sourceObject": {
"apiGroup": "apps",
"apiVersion": "v1",
"name": "nginx-deployment-five",
"namespace": "test-namespace-five",
"resource": "deployments",
"resourceVersion": "61949",
"uid": "5eb6d1d1-b694-4679-a482-d453bcd5317f"
},
"oldSourceObject": {
"apiGroup": "apps",
"apiVersion": "v1",
"name": "nginx-deployment-five",
"namespace": "test-namespace-five",
"resource": "deployments",
"resourceVersion": "61949",
"uid": "5eb6d1d1-b694-4679-a482-d453bcd5317f"
},
"lastUpdate": {
"time": "2023-11-25T13:12:28.251894531Z",
"userUID": "165d3e9f-04f4-418e-863f-07203389b51e",
"username": "kubernetes-admin"
},
"event": {
"type": "update"
}
}
An object was uploaded to a recovery bucket.
{
"level": "info",
"timestamp": "2023-11-28T18:05:27.593493962Z",
"msg": "object uploaded in bucket",
"sourceObject": {
"apiGroup": "apps",
"apiVersion": "v1",
"name": "helloworld",
"namespace": "test-namespace-one",
"resource": "deployments",
"resourceVersion": "936",
"uid": "7c2ac690-3279-43ca-b14e-57b6d57e78e1"
},
"oldSourceObject": {
"apiGroup": "apps",
"apiVersion": "v1",
"name": "helloworld",
"namespace": "test-namespace-one",
"resource": "deployments",
"resourceVersion": "936",
"uid": "7c2ac690-3279-43ca-b14e-57b6d57e78e1"
},
"process": {
"id": "processor",
"consumerID": "event-processor-n74"
},
"bucket": {
"name": "bucket-dev",
"namespace": "dr-config",
"resourceVersion": "91006",
"uid": "47b50013-3058-4283-8c0d-ea3a3022a339"
},
"bucketObject": {
"path": "dr-config/pre/apps-v1-deployments/test-namespace-one.helloworld"
},
"lastUpdate": {
"time": "2023-11-25T13:12:29.625399813Z",
"userUID": "165d3e9f-04f4-418e-863f-07203389b51e",
"username": "kubernetes-admin"
}
}
Managing logs
Messages structure vary depending on the operation that originated it.
The sourceCluster and destinationCluster are only present for operations that required direct access to either cluster. For the former, only messages originating from either the eventsListener, processor or reconciler services can include it in their logs. The latter will only be present in synchronizer or reconciler logs messages. These parameters will not be present for internal messages such as those coming from the nats since there is no direct connection with either cluster.
oldSourceObject is the previous state of the object when performing an update operation. It is not present in other types.
When the bucket and bucketObject parameters are present, the operation is performed against the indicated bucket without any involvement of the source and destination clusters. For create operations, an object was uploaded for the first time to the bucket, for updates an existing one is modified and for delete an object was deleted from the specified bucket.
These characteristics can be exploited to improve log searches by narrowing down the messages to those that are relevant at the moment. Serving as an example, the following command will output only those logs that affect the source managed cluster by filtering the messages that lack the sourceCluster.
kubectl -n dr-config logs pre-eventslistener-74bc689665-fwsjc | jq '. | select(.sourceCluster != null)'
This could be useful when trying to debug and solve connection issues that might arise.
Log messages
The log message is located in the msg parameter. It can be read and interpreted to establish the severity of the log. The following tables group every different log message depending on whether it should be treated as error or informative.
Error messages
| msg |
|---|
| “error reading server groups and resources” |
| “error reading resources for group version” |
| “error getting namespace from cluster” |
| “error creating namespace in cluster” |
| “error getting object from cluster” |
| “error creating object in cluster” |
| “error updating object in cluster” |
| “error listing objects in cluster” |
| “error deleting object in cluster” |
| “error uploading object in bucket” |
| “error deleting object form bucket” |
| “error getting object from bucket” |
Informative messages
Not found objects are not errors
Errors regarding not found objects do not represent errors but rather normal behaviour while synchronizing objects not present in one of the clusters.| msg |
|---|
| “reading server groups and resources” |
| “server group and resources read from cluster” |
| “reading resources for group version” |
| “resource group version not found” |
| “group resource version found” |
| “reading namespace from cluster” |
| “namespace not found in cluster” |
| “namespace read from cluster” |
| “creating namespace from cluster” |
| “namespace already exists in cluster” |
| “namespace created in cluster” |
| “reading object from cluster” |
| “object not found in cluster” |
| “object read from cluster” |
| “creating object in cluster” |
| “object created in cluster” |
| “updating object in cluster” |
| “object updated in cluster” |
| “deleting object in cluster” |
| “object deleted in cluster” |
| “listing objects in cluster” |
| “list objects not found in cluster” |
| “listed objects in cluster” |
| “uploading object in bucket” |
| “object uploaded in bucket” |
| “deleting object from bucket” |
| “object deleted from bucket” |
| “getting object from bucket” |
| “object got from bucket” |
| “listing object from bucket” |
3 - Granafa setup
Resiliency Operator offers the option of leveraging an existing Grafana installation to monitor the state of the synchronization and recovery process. Users can incorporate the provided visualizations to their workflows in a transparent manner without affecting their operability.
1. Requirements
Grafana Operator
The operator installation includes the necessary tools to extract the information from it. To view that information with the official dashboard, is required that the management cluster has the Grafana Operator installed.
Astronetes Disaster Recovery Operator supports Grafana v4 and Grafana v5.
2a. Using Grafana Operator v4
Create the GrafanaDashboard from the release manifests:
kubectl apply -f https://astronetes.io/deploy/disaster-recovery-operator/v0.11.0/grafana-v4-dashboard.yaml
2b. Using Grafana Operator v5
Create the GrafanaDashboard from the release manifests:
kubectl apply -f https://astronetes.io/deploy/disaster-recovery-operator/v0.11.0/grafana-v5-dashboard.yaml
3. Working with the dashboard
The dashboard shows detailed information about the write, read and computing processes alongside a general overview of the health of the operator.
General view of the status of the operator:
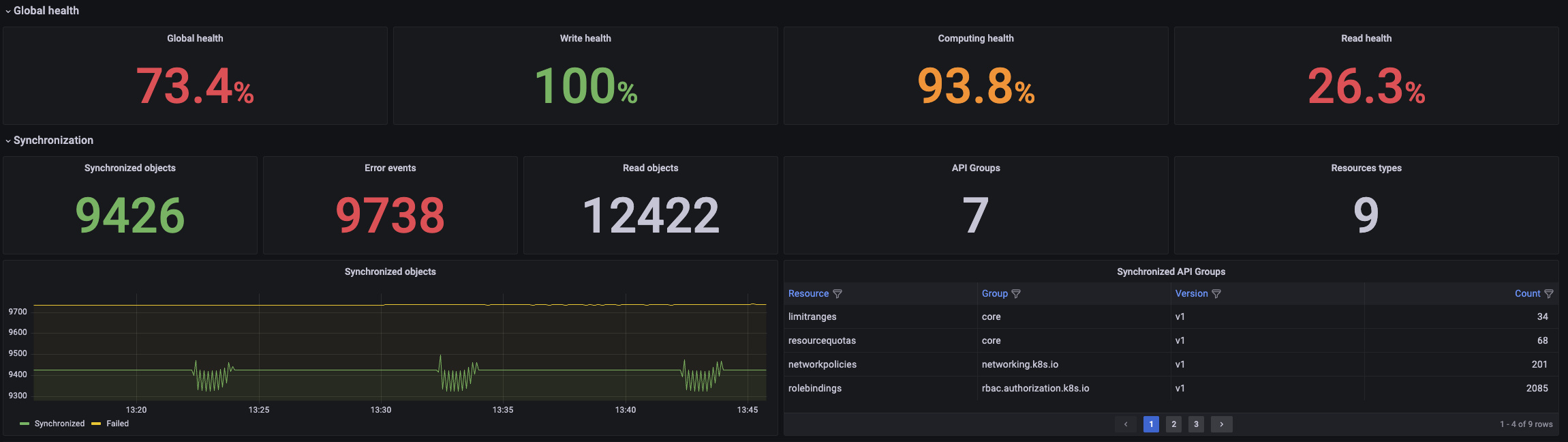
The dashboard can be filtered attending the following characteristics:
- Namespace. Only shows information related to the
LiveSynchronizationsin a specified namespace. - Recovery Plan. Filters by a specific
LiveSynchronizaton. - Object Namespace. Only shows information of the objects located in a given namespace regardless their associated
LiveSynchronization. - Object API Group. Objects are filtered attending to the API Group that they belong to.
Filters can be combined to get more specific results e.g. Getting the networking related objects that belong to a LiveSynchronization that is deployed in a namespace.